Which wins out in the conflict between algorithmic and manual trading for modern traders? While algorithmic trading uses speed and data analysis to make frequent decisions, manual trading places a higher value on human experience and human intuition.
This article breaks down the main advantages and disadvantages of each to assist you in determining which approach will best suit your trading style and maximize your trading performance.
Key Takeaways
- Compared to algorithmic trading, which is faster and less of emotional decision-making but may experience system failures and lack human judgment.
- Manual trading is more flexible and depends on personal experience, but it is also slower in execution and more prone to emotional bias.
- Algorithmic trading involves the use of intricate mathematical models to execute trades at high speeds and volumes through the use of platforms such as Tradetron , Meta Trader and Ninja Trader. However, this approach entails significant technical knowledge, operational risks, and the possibility of over-optimization.
- The secret to successful trading is to strike a balance between risk management techniques and market flexibility.
Exploring the Spectrum of Trading: Manual vs Algorithmic

Both manual and algorithmic trading methods are available to traders as they attempt to make their way through the complex web of the financial market.
As the name implies, manual trading is a hands-on strategy in which traders manually open and close positions according to their analysis, knowledge and instincts.
On the other hand, algorithmic trading is a sophisticated strategy that uses pre-established algorithms to automate trade analysis and execution .Although many people do the analysis part manually and execution part algorithmically.
The former takes more time and practical effort, but it requires less technical knowledge. However, algorithmic trading greatly lessens the need for continuous monitoring, though it still calls for technical know-how and specialized infrastructure.
The choice between these two methods depends on various factors such as individual trading style, objectives, and the specific market conditions at play.
The Essence of Manual Trading
The ability of the trader to meticulously study market trends is the foundation with which manual trading is built.
Manual trader can consider following factors for making his trading decisions.
- Fundamental Analysis : For the purpose of determining the intrinsic value of a company trader can take into consideration the fundamental analysis, it involves the compilation of financial statements, taking into account external influences, industry trends, and events.
- Qualitative and quantitative data : For the purpose of making well-informed decisions, manual traders can utilize a combination of qualitative and quantitative data, such as the value of the brand and management actions, as well as financial statistics.
- Sectoral Trend : For the purpose of gaining an understanding of long-term market patterns, they employ either a top-down method that concentrates on macroeconomic issues or a bottom-up approach that focuses on specific firm characteristics.
- Technical Analysis : Through the utilization of technical indicators like the stochastic oscillator, ADX, and RSI, they are able to determine the direction of the trend, momentum, and overbought or oversold circumstances.
This provides them with essential insights into the psychology of the market as well as the supply and demand dynamics of securities.
Unpacking Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading makes use of computer programs to automate the trading process, hence removing human biases from the trading process.
Trading algorithms utilize a wide variety of algorithms, including the following:
- Shortfall algorithms (Implementation Shortfall): Aim to reduce the cost difference between the decision price and final execution price.
- VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price): Ensure trades are executed near the market volume average price.
- Basket algorithms: Optimize the execution of trades across a portfolio of securities.
- Quantitative analysis: Utilizes statistical models for objective, data-driven trading decisions.
- Customizable trading bots: Designed with adjustable parameters to suit specific strategies and risk levels.
This list is exhaustive but does not include all algorithm types.

Human vs Machine
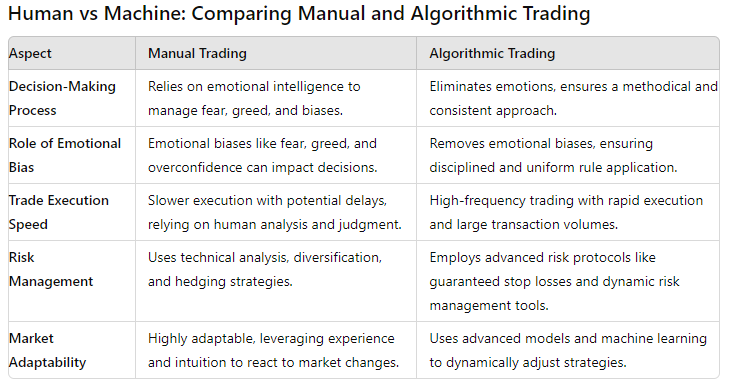
#1 The Decision-Making Process
The manner by which decisions are made is one important difference between algorithmic and human trading.
To recognize, control, and understand one’s own emotions as well as those of others, emotional intelligence is crucial in manual trading.
Fear and greed, for example, have a powerful effect on trading decisions and can cause impulsive and illogical trading judgments.
Proficient traders set themselves apart by their capacity to control volatile emotions and adjust to shifting market circumstances.
The elimination of emotions and prejudices, on the other hand, results in a more methodical and consistently applied approach to decision-making through algorithmic trading.
The Role of Emotional Bias in Trading
For manual traders, emotional biases are frequently a major obstacle. Fear and greed can cause traders to stray from their plans, making rash and unreasonable trading decisions.
To succeed in manual trading, traders must develop their emotional intelligence by identifying and controlling disruptive emotions as well as becoming self-aware of their emotional triggers.
Another emotional bias that might cause traders to trade excessively is overconfidence, which stems from the mistaken idea that one can influence market outcomes and frequently produces less than ideal investing outcomes.
Traders can learn how emotions influence their decisions and keep a disciplined approach to risk management by using strategies like reflective journaling.
Automated Systems: Removing the Emotion
The emotional component of trading is eliminated by algorithmic trading systems.
Emotional reactions could lead to departures from the coded strategies that these automated systems abide by.
Algorithmic trading ensures uniform application of trading rules
It eliminates the possibility of errors frequently caused by psychological variables, and promotes a more disciplined approach to trading by removing emotions from the equation.
It is important to remember that these systems have limits as well.
For example, they are unable to execute trades without human judgment, which may not be able to take judgement in special circumstances such as Flash crash.
#2 Speed and Precision: Executing Trades in Real-Time
Manual and algorithmic trading differ greatly in terms of trade execution speed and accuracy.
Unlike conventional trading techniques, algorithmic trading executes numerous trades at once and does it at a breakneck speed.
By automating the process of assessing and executing trade orders, algo trading reduces the need for continual human oversight and increases speed and efficiency.
Conversely, Traditional trading is less effective and slower at executing deals in real-time; manual traders frequently experience delays that lead to lost chances.
Manual Trade Execution
Unlike automated trading, which uses computer systems to make these decisions, manual trading requires human decision-making when entering and exiting transactions.
In manual trading, the trader’s analysis, judgment, and expertise serve as the primary determinants of what to purchase and sell.
Manual traders retain the final say over whether to enter or exit deals, even if computer algorithms can be used to aggregate market data and generate alerts for possible trading opportunities.
High-Frequency Trading with Algorithms

In the trading industry, High-Frequency Trading (HFT) is the pinnacle of speed.
HFT, which uses specialized computers built for the highest execution rates, is known for its extraordinarily high transaction volumes and short investment horizons.
By end of 2024, computers will have executed more than 80% of all deals on the financial markets, therefore manual traders will face a great deal of competition from HFT’s speed and efficiency.
In a matter of milliseconds, HFT algorithms can examine equities on the stock market and spot developing trends. Based on this analysis, a huge number of buy orders can be executed quickly.
#3 Balancing Risk and Reward: Risk Management in Trading
Successfully navigating the financial markets requires striking a balance between risk and reward, much like when walking a tightrope.
In order to stay afloat, both algorithmic and manual traders use a variety of risk management techniques.
To plan trade exits and safeguard investments, manual traders utilize take-profit and stop-loss levels derived from technical analysis tools.
On the other hand, algo trading systems consist of:
- Risk-aversion criteria that are in line with the risk tolerance of traders.
- Clients Complex algorithms that control the magnitude of trades To manage portfolio risk.
Risk Management in Manual Trading
A variety of risk management techniques are available to manual traders.
To plan trade exits and safeguard investments, they employ stop losses and take-profit points based on technical analysis techniques such as moving averages and support/resistance levels.
Another popular tactic is diversification, which helps distribute assets throughout various market capitalizations, industrial sectors, and geographical areas to reduce linked risks.
In order to guard against stock position losses, manual traders also use hedging techniques like purchasing downside put options.
Maintaining a good risk to reward ratio is also essential for long-term profitability, even in the event of a 50% win rate.
Algo Trading and Advanced Risk Protocols
Algorithmic trading systems bring a more advanced approach to risk management. These systems use specific tools like guaranteed stop losses, two-lot systems for taking partial profits, normal and trailing stop losses for risk control that provide dynamic risk management.
Maintaining discipline through advanced risk management strategies is critical in algo trading as it helps in consistently mitigating risks and protects from emotional decision-making.
These systems also offer robust back-testing capabilities, enabling traders to test strategies against historical data, validating and refining their trading models.
#4 Adapting to Market Conditions: Flexibility in Trading Styles
One of the hallmarks of a successful trader is the ability to adapt to changing market conditions. Flexibility and adaptability in trading styles are crucial in navigating the financial markets.
Many traders adopt a hybrid approach that leverages the strengths of both manual and algorithmic trading to enhance their adaptability to changing market conditions.
Experimenting with both methods using small investments can help traders understand which approach better aligns with their trading goals and the prevailing market conditions.
Manual Trading Adaptability
A manual trader’s strength lies in the ability to:
- Adapt to changing market conditions swiftly
- Maintain ultimate control over every trading decision
- React and adapt swiftly to market changes
- Use their experience, intuition, and judgment to adjust their strategies according to market trends, economic news, and technical indicators.
This adaptability allows them to take advantage of their expertise and control risk while anticipating market trends.
Algorithmic Response to Market Dynamics

Algorithmic trading systems are not left behind when it comes to adaptability. Advanced statistical models and machine learning algorithms analyze historical and real-time data to adapt algo trading strategies dynamically, optimizing performance across various market conditions.
The integration of machine learning and AI enables algo trading software to analyze large datasets and adapt trading strategies, predicting market movements with a higher level of accuracy.
The Human Touch: Advantages and Disadvantages of Manual Trading
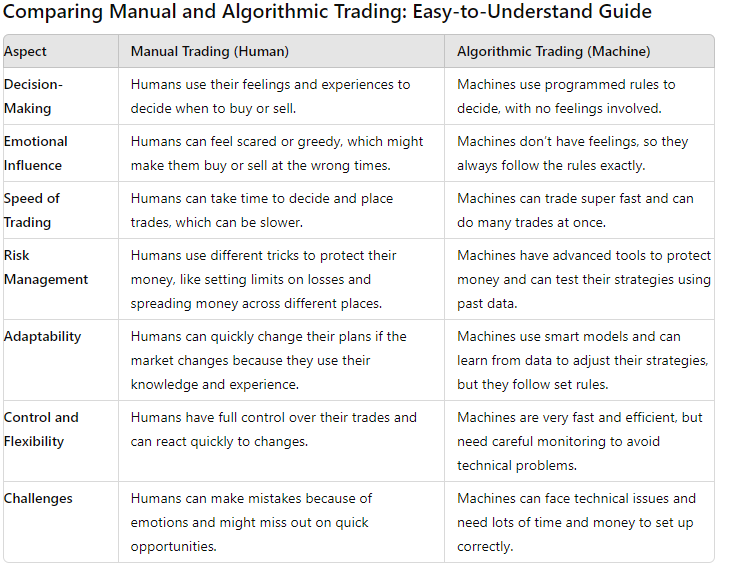
While algorithmic trading offers numerous advantages, manual trading also brings its unique strengths to the table, such as flexibility and customization.
However, manual trading is not without its challenges. Emotional biases and slower reaction times compared to algorithmic trading systems can pose significant hurdles for manual traders.
Benefits of Being a Manual Trader
Manual trading offers a number of advantages.
Manual traders maintain ultimate control over every trading decision, allowing them to react and adapt swiftly to market changes. Experienced traders can apply their deep market knowledge to inform their trades, taking advantage of their expertise to control risk and anticipate market trends.
The flexibility of manual trading lies in its adaptability, allowing the use of a diverse set of technical and fundamental analysis tools to tailor trading strategies to the current market scenario.
Challenges Faced by Manual Traders
Despite its advantages, manual trading comes with its own set of challenges.
Manual traders are susceptible to emotional biases, which can cloud judgment and lead to suboptimal trading decisions.
Slower reaction times in manual trading may result in delays in executing trades, causing missed opportunities compared to algorithmic trading systems.
Recognizing and mitigating the impacts of emotional biases and slower reaction times is crucial for manual traders to improve their trading outcomes.
The Algorithmic Edge: Advantages and Disadvantages of Algo Trading
While manual trading offers the advantage of customizability and control, algorithmic trading brings speed, efficiency, and the ability to capitalize on multiple trading opportunities to the table. However, algorithmic trading comes with its own set of challenges, such as system failures and the complexity of developing profitable strategies.
Strengths of Algorithmic Trading Systems
Algorithmic trading systems offer numerous advantages.
- They significantly outperform manual trading in terms of speed and efficiency, enabling quicker analysis and execution of trades.
- Their ability to analyze large datasets and adjust trading strategies makes them a valuable tool for traders looking to capitalize on more opportunities at better prices.
- Reduced transaction costs are another benefit of algo trading as it doesn’t require continual market monitoring, saving both time and the opportunity cost of manual oversight.
- Algo trading also enhances accuracy by avoiding common human errors in trade entries, resulting in more reliable transaction processing.
Limitations and Risks of Algo Trading
Despite its numerous advantages algorithmic trading suffers from few disadvantages as well
- Algorithmic trading systems can suffer from technical risks, including system failures and data inaccuracies, which may lead to incorrect trading decisions and severe financial losses.
- The development and continuous updating of algorithmic trading systems can be highly complex and costly, presenting a significant barrier to entry for individual traders and small firms.
- Operational risks such as regulatory compliance, cybersecurity, and liquidity issues require meticulous management, and the possibility of over-optimization may reduce the effectiveness of the trading algorithms.
If you want to understand strategies for mitigating risk in Algorithmic trading : Click here
In conclusion, both manual trading and algorithmic trading bring their unique advantages and challenges to the table.
While manual trading offers control and adaptability, it also comes with the hurdles of emotional biases and slower reaction times.
On the other hand, algorithmic trading provides speed and efficiency but is not without its risks, such as system failures and the complexity of developing profitable strategies.
Ultimately, the choice between manual and algorithmic trading depends on individual preferences, trading goals, and the specific market conditions.
As technology continues to evolve, it is crucial for traders to stay agile, harnessing the strengths of both methods to navigate the financial market’s dynamic landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is trading using algorithms more profitable?
When applied correctly and with appropriate risk management, algorithmic trading can be profitable. It provides a more methodical and disciplined approach, improving trade execution efficiency. Think about putting effective tactics and methods of validation into practice for success.
What is the main distinction between algorithmic and manual trading?
Manual trading requires human intervention, whereas algorithmic trading automates trades using pre-established algorithms.
This is the main distinction between algorithmic and manual trading. This indicates that while algorithmic trading depends on automation to execute trades effectively, manual trading necessitates making decisions by hand.
Which risk-management techniques are applied in manual trading?
A manual trader can employ stop losses and take-profit points based on technical analysis tools for trade exits and investment protection. Diversifying portfolios and using hedging strategies can also help mitigate risk.
Does algorithmic trading yield higher profits?
With the right application and risk management, algorithmic trading can be profitable. It increases the effectiveness of trade execution by providing a more methodical and disciplined approach. For success, think about putting the appropriate plans and techniques for validation into action.
You can read the below mentioned blog for better understanding :
Does Algorithmic Trading Work? Unpacking the Efficiency and Profit Potential
What are the challenges associated with algorithmic trading?
Problems with algorithmic trading include complicated system development, operational issues like cybersecurity and regulatory compliance, and technical risks. Effectively mitigating these challenges requires careful management.




