Even though algorithmic trading has changed the way we interact with the financial markets, it also brings new risks of algorithmic trading that might destabilize individual investments and the market overall.
In this article, we will examine these potential risks of algorithmic trading in order to provide you the tools to evaluate algorithms and their applications in financial industry with confidence.
Key Takeaways
- There is a real risk that algorithmic trading, and especially high-frequency trading, might increase market volatility, cause system failures, and make markets more vulnerable to manipulation, all of which can result in substantial and quick financial losses.
- Complex algorithms and accurate data are the backbone of algorithmic trading. Nevertheless, poor trading decisions and monetary losses can occur from an excessive dependence on algorithms, inaccurate data, and a lack of transparency.
- In order to reduce the risks associated with algorithmic trading and keep the market stable, it is essential to implement risk management strategies that include strong safeguards, human supervision, and compliance with changing regulatory frameworks.
Unveiling the Risks: A Deep Dive into Algorithmic Trading’s Dark Side

Market Volatility and Rapid Execution
There is a substantial danger of market volatility when using algorithmic trading, particularly when using high-frequency trading. Traders run the risk of losing money due to the unpredictability of the results.
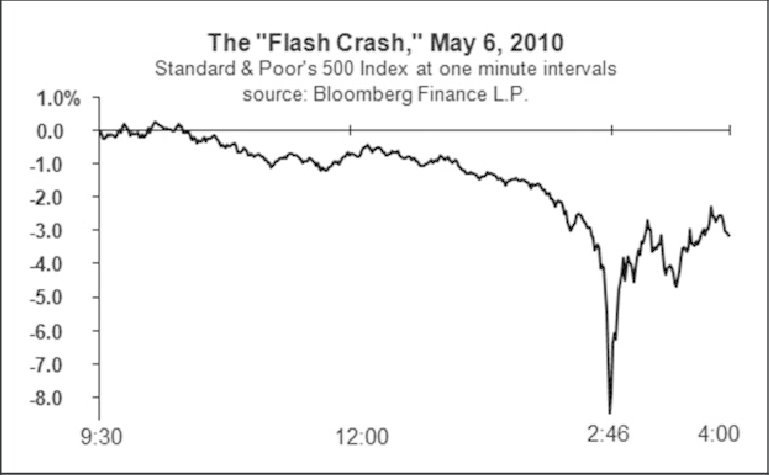
Quick trade execution can cause market storms, which can put a lot of money at risk. When high-frequency trading caused the market crash known as the Flash Crash in 2010, this became very clear.
System Failures: When Technology Falters
In the same way that a computer can crash from a small glitch, algorithmic trading strategies can have their financial outcomes ruined if system failures occur.
A great deal of problems could arise if the electronic systems that are so heavily relied upon suddenly stopped working. Especially in high-frequency trading, where mistakes can quickly lead to huge losses.
Another factor that raises the possibility of a systemic failure is the inherent complexity of financial algorithms. This might cause quick monetary losses and is often triggered by unsavory market occurrences.
In algorithmic trading, technical risks can arise from data inaccuracies, programming mistakes, or system failures. These issues can lead to incorrect trading signals and budgetary losses.
The Threat of Market Manipulation
Manipulation of the market is another potential threat in the realm of algo trading. Intuitive algorithms can be manipulated to make trades based on misleading market conditions.
Market perceptions and prices can be manipulated through tactics like spoofing and layering, which entail placing and then canceling enormous volumes of orders.
Add insult to injury, the high volume of orders that are quickly canceled makes it hard to tell the difference between legitimate and manipulative trading activities.
The dangers of market manipulation can be amplified by behavioral biases like overconfidence, and by feedback loops that can be created by flawed data analysis.
The Complexity of Algorithms and Data Reliability

Problems with data reliability and the complexity of trading algorithms are both revealed when one investigates algorithmic trading in further depth.
Although these algorithms are essential to algorithmic trading, they also pose a threat of complacency if traders become too comfortable with them and fail to change them enough to account for changing market conditions.
Advanced Algorithms and Inherent Risks
Automated trading algorithms, in particular when used for high-frequency trading, pose their own distinct dangers. If these intricate algorithms make a mistake and misjudge current market conditions, it could trigger a chain reaction that ends badly for the financial markets.
Conversely, ethical and legal concerns may arise due to the lack of accountability and transparency brought about by black-box algorithms that utilize AI and ML in the trading process.
Trading algorithms that are over-optimized using past data run the risk of failing under sudden changes in the market.
Interesting watch on risks of High Frequency Trading !!
Data Analysis: The Pitfalls of Inaccurate or Incomplete Data
Data can be a powerful tool in algorithmic trading if used properly.
However if data is not accurate it can be very derimental.
For example, if models are built using out-of-date or incorrect data, it could distort market sentiment and cause traders to make uninformed decisions. This may lead to less-than-ideal trading decisions and feasible monetary setbacks.
Alternatively, algorithms could make market judgments without a comprehensive perspective if they are given incomplete data. Because of this, the algorithm may fail to take into account important cues that could change the course of the trade.
Algorithmic trading strategies are very sensitive to data completeness and quality. Thus, these factors are fundamental for guaranteeing their efficacy and precision.
Regulatory Challenges and Compliance Risks in Algorithmic Trading

Along with the maze of algorithmic trading comes a plethora of compliance and regulatory hurdles.
There are current initiatives to update enforcement mechanisms and counter manipulative trading practices; traders would do well to monitor regulatory developments and adjust their trading tactics accordingly.
Navigating Regulatory Changes
In light of these regulatory shifts, algorithmic trading firms will need to establish robust compliance policies to safeguard the market and forestall any unjustified interference. Below are a few suggestions for best practices:
- To mitigate the effects of algorithmic trading strategies, a multidisciplinary group shall be formed.
- Making use of stringent methods of oversight and management.
- Making sure compliance policies are up-to-date and reviewed often to meet regulatory standards
Companies can successfully mitigate algorithmic trading risks and keep the market honest when they use these practices to make trades.
In addition, businesses must disclose their algorithmic trading tactics and compliance precautions to the appropriate trading venues and their Designated Regulatory Authority.
To ensure compliance with current regulatory standards, it is crucial to continuously assess algorithmic trading activities following modifications.
The Importance of Continuous Monitoring for Compliance
In order to keep regulatory adherence in trading and minimize risk, continuous compliance monitoring is crucial, along with navigating regulatory changes.
The only way to stop market manipulation and accidental losses is with a compliance control system that includes trade monitoring, user access control, and credit risk and market monitoring before and after trades.
Legal requirements also require firms to make sure documentation is easily accessible to those in charge of algorithmic trading oversight.
The developers of algorithmic strategies must maintain constant communication with the compliance staff in order to guarantee continuous adherence to all trading regulations.
Risk Management Strategies for Algorithmic Traders

Risk management is still the most important part of trading, even when using algorithms.
The intricate world of algorithmic trading can be successfully navigated by traders who employ strong safeguards and strike a balance between human knowledge and automated processes.
Implementing Robust Risk Management Measures
The increased market volatility and unpredictability that may result from high-speed algorithmic trading can be mitigated through effective risk management.
Organizations must implement a thorough program for assessing and responding to risks in order to monitor their trading activities and adjust to the changing threats posed by algorithmic strategies.
To lessen the blow, you can use stop-loss orders to close your position automatically whenever the market turns against you, saving you from even more losses.
One important safeguard against the dangers of high-frequency algorithmic trading and the possibility of systemic market failures is the use of “kill switches” for trading companies and “circuit breakers” for the stock market.
Human Oversight: Balancing Automation with Expertise
As important as automation is as a feature of algorithmic trading, human oversight is equally important.
When dealing with market disruptions, experienced traders must keep a close eye on algorithms to make sure they are behaving as predicted.
For algorithmic and automated trading to run well, it is crucial to have a competent team overseeing the interface between automated systems and human knowledge.
Traders can unlock more flexibility and make live adjustments to their strategies in response to market conditions that algorithms can’t see coming by combining algorithmic trading with human judgment.
Algorithmic Trading and the Broader Financial System

The wider financial system is profoundly affected by algorithmic trading, which goes beyond the influence of individual strategies.
It is critical to comprehend the systemic significance of algorithmic trading because it constitutes a substantial fraction of all trades.
Market Makers and Their Role in Stability
The stability of stock prices is a result of market makers, who act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers in the financial markets.
Market makers in the realm of algorithmic trading have state-of-the-art tools at their disposal, which enable them to efficiently execute orders and swiftly process large volumes of transactions, thereby enhancing their ability to stabilize the market.
Systemic Risks: The Domino Effect in Finance
Algorithmic trading has many positive uses, but it also introduces new threats to the financial system. Coordinated erroneous trades and increased market volatility can result from the widespread use of identical algorithms.
Because shocks can be swiftly transmitted from one market to another, high-frequency trading has the ability to increase systemic risk.
The Flash Crash of 2010 and similar events show how algorithmic trading can cause financial systemic risks.
Summary
Finally, while algorithmic trading has many advantages, it does not come without risks.
Traders must understand the risks, which range from market volatility and manipulative trading tactics to technological failures and data reliability issues.
These risks can be effectively mitigated by implementing strong risk management strategies, managing regulatory changes, and balancing automation with human oversight.
As the financial markets evolve, staying informed about these risks and strategies is critical for navigating the complex world of algorithmic trading.
Frequently Asked Questions
How risky is algorithmic trading?
Overfitting strategies to past data is one major risk associated with algorithmic trading. Another is the reliance on complicated technology, which can fail, crash, or be compromised (Investopedia). Market volatility, execution mistakes, and possible losses in real-time markets are all possible outcomes of these risks.
What are the operational risks of algorithmic trading?
Market volatility, technical failures, and over-optimization are operational risks associated with algorithmic trading that can impact market performance through delays, errors, losses, and unwanted trades.
Significant disruptions and possible financial losses can occur if the complex technology upon which it depends fails, crashes, or is hacked.
What are the pros and cons of algorithm trading?
While there are many benefits to algorithmic trading, such as speed, efficiency, and risk management, there is also a risk of over-optimization and reliance on data. On top of that, it could make bad market trends even worse. To sum up, algorithm trading success requires full consideration of the benefits and drawbacks.
How does high-frequency trading contribute to market volatility?
HFT helps increase market liquidity.
What measures can be implemented to manage risks in algorithmic trading?
Algorithmic traders can mitigate their exposure to risk by using stop-loss, take-profit, limit, and “kill switch” orders. You can safeguard your investments and lessen the impact of possible risks by implementing these measures.




