You’re sitting at your computer, watching numbers flicker on a screen. One moment, the price of a stock is up, the next, it’s down. You make a quick decision, hit a button, and boom—you’ve just made a trade!
But here’s the catch: before the day ends, you’ll need to sell that stock. No holding onto it overnight, no waiting for weeks or months to see if you made a smart choice.
This is day trading, the fast-paced world where every second counts and traders aim to make a quick profit.
In this blog, we’ll take you through the thrilling world of day trading, explain how it works, who does it, and whether it’s something you can do to earn a living.
Don’t worry, we’ll keep things simple and fun—no need to be a financial expert to understand!
By the end, you’ll know exactly what day trading is and whether it might be the right fit for you.
So, ready to dive in?
Let’s go!

What is Day Trading?
Imagine a game where you buy and sell toys, but you have to sell them by the end of the day. That’s kind of what day trading is! Instead of toys, though, day traders buy and sell things like stocks (which are little pieces of companies), cryptocurrencies (think digital money like Bitcoin), or foreign currencies.
The goal? Make a quick profit by taking advantage of small changes in prices during the day.
Day traders are a bit like busy bees—they work fast, buying and selling multiple times in just a few hours.
Unlike other people who invest for the long run, day traders don’t keep their stocks or currencies overnight. They want to end the day with no “open” trades because holding on to anything overnight is risky. Prices might go up or down while they’re asleep!
Who Are Day Traders?
In Simple words Day Traders are traders operating on the Daily Timeframe. They make quick decisions and are always on the lookout for the next move to make quick bucks. They Don’t Hold Positions overnight.
Some day traders are regular people working from home, using their computers and phones to trade. They could be someone like your neighbor or even your cousin. Other day traders are professionals who work for big companies, and their full-time job is trading all day long.
Alert : Day Trading is a full time Job and if done part-time its a hobby.
Day traders need to have a few special superpowers, like:
- Fast decision-making: Prices move fast, so they need to act quickly.
- Cool under pressure: They can’t get scared or too excited when prices change.
- Good at math: They don’t need to be wizards, but knowing a bit about numbers helps.
They also use tools like charts, graphs, and fancy computer programs to predict when prices will move up or down. However these are not exclusive to Day Trading.
How Does Day Trading Work?
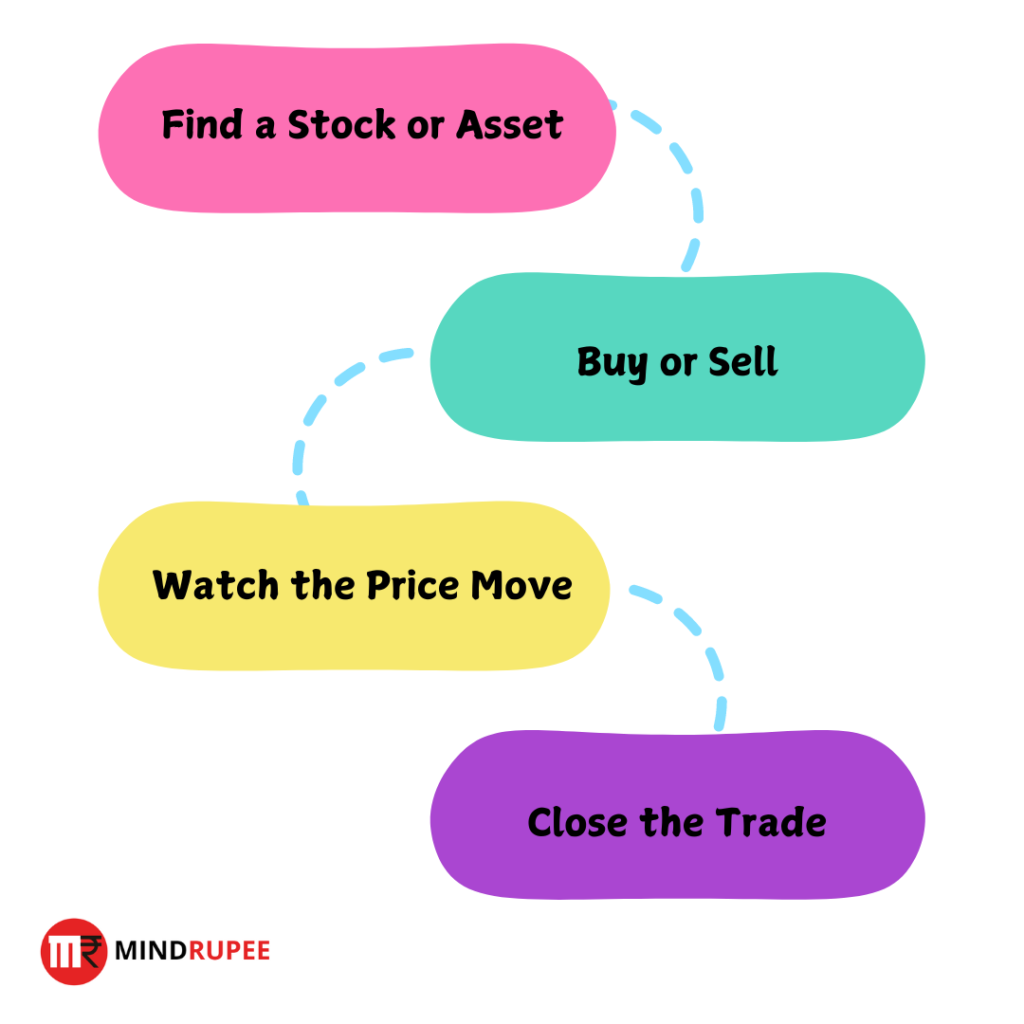
Let’s break down day trading :
- Find a Stock or Asset: Day traders pick a stock, currency, or digital coin that looks like it might move in price. That could be based on bounce from Support , Momentum , Volume burst or some other criteria.
- Buy or Sell: They place a “buy” or “sell” order based on whether they think the price will go up or down.
- Watch the Price Move: Now, they wait and watch the price move. This could take seconds, minutes, or a few hours.
- Close the Trade: Once the price has moved the way they want (hopefully!) or if the stoploss is hit, they “close” the trade by selling the asset they bought.
The secret sauce here is timing. Day traders need to get in and out at just the right time to make a profit, which means they need to be sharp-eyed and quick-fingered.
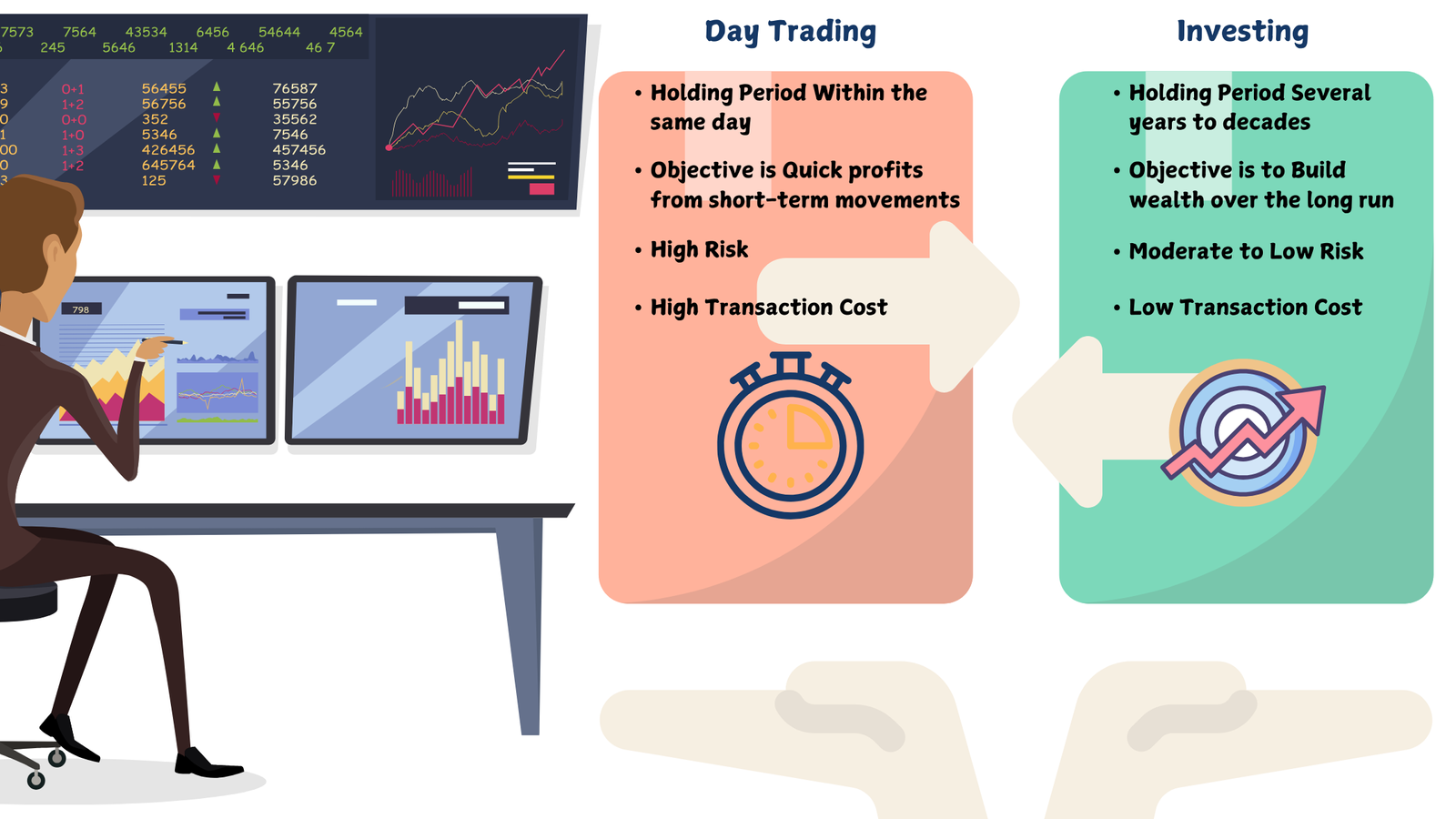
Day Trading Vs. Other Types of Trading
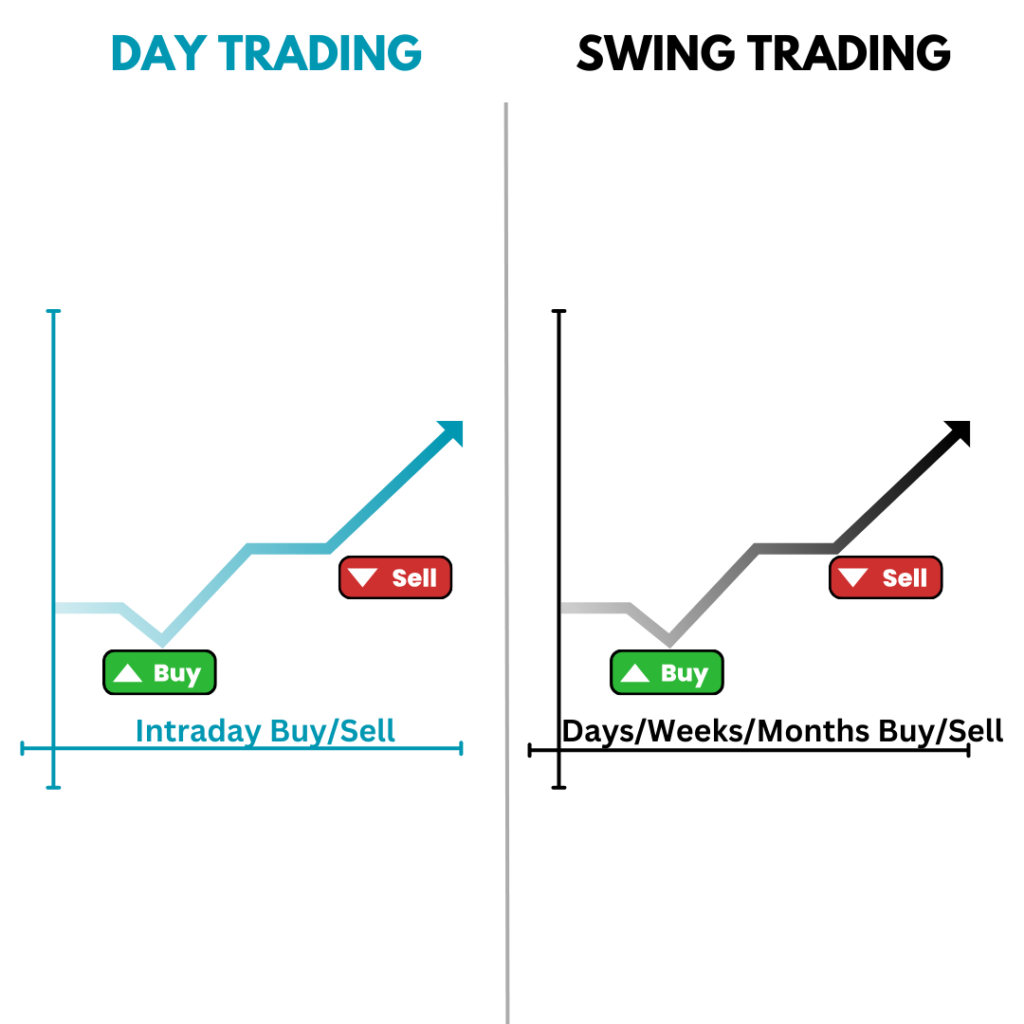
So, how does day trading stack up against other types of trading? Let’s break it down with an easy comparison:
- Day Trading: Like we said, you buy and sell in one day—no sleeping on it!
- Swing Trading: Swing traders keep their investments for several days or even weeks, waiting for a bigger price change.
- Position Trading: These traders hold on to their investments for months or even years. It’s a long game for them.
- Long-Term Investing: This is like planting a tree and waiting years for it to grow. Investors hold on to their stocks for a long, long time, sometimes even decades.
In a nutshell, day trading is a quick and energetic sprint, while other types of trading are more like a marathon.
| Type of Trading | Holding Period | Objective | Risk Level | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day Trading | Within the same day | Quick profits from short-term movements | High (fast-paced trades) | Buying and selling a stock within hours |
| Swing Trading | Several days to weeks | Profit from medium-term trends | Moderate (less intense) | Holding a stock for a few weeks, expecting a jump |
| Position Trading | Months to years | Profit from long-term trends | Lower (longer horizon) | Holding a stock for a year or more |
| Long-Term Investing | Several years to decades | Build wealth over the long run | Lowest (focus on growth) | Buying stocks for retirement and holding for decades |
What is the Minimum Capital Required to Day Trade?
To get started with day trading, you’ll need some pocket money—except in this case, it’s more like grown-up pocket money. In many countries, like the U.S., you’ll need at least $25,000 if you want to day trade stocks regularly. This is because of the Pattern Day Trader Rule, which says you must have that amount in your account to trade more than three times in a week.
But don’t worry! You don’t need that much if you want to trade other things like cryptocurrencies or forex (foreign currencies). In India, for example, you could start with as little as ₹50,000 to ₹100,000 for day trading stocks, but more is always better because it helps cover any small losses you might face while learning.
Can You Make a Living Day Trading?
Ah, the million-dollar question! Can day trading pay the bills and keep you sipping coconut water on a beach?
Well, yes and no. Some people do make a living from day trading, but it’s not as easy as it sounds. It takes a lot of practice, knowledge, and discipline. Most beginners lose money at first because they don’t know how to manage risks. Think of it like trying to ride a bike—you might fall a few times before you get the hang of it.
To make a living, day traders need to:
- Be Consistent: You won’t win every time, but winning more than losing is the goal.
- Stay Focused: Distractions are a trader’s worst enemy.
- Manage Risk: Don’t bet the farm on one trade. It’s better to make small, steady profits.
Also its very important to keep realistic expectations. If you want to Double your money Every month. Stay away you are going to loose. Expecting 1~3% per Month is Good Number.
So as a thumb rule you need a 50 times your monthly Expense as the Trading capital to start making Living out of it.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Day Trading
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Quick profits (if done right) | High risk—losses can happen quickly |
| No overnight risk | Stressful and requires full attention |
| You control your trades | Can be addictive |
| Can be done from home | Requires a lot of practice and skill |
| No need for long-term predictions | Brokerage fees can add up |
Interesting Facts and Figures Regarding Day Trading in India
- Between 80-95% of day traders fail
- A whopping 97% of day traders lose money in less than a year
- Less than 1% of day traders consistently profit
- Day traders lost $1.14 billion during the pandemic, with an additional $4.13 billion in trading costs
- Profitable traders account for only 12% of all day trading activities
- The average day trader’s return rate is just 10%
- There are 9.6 million traders around the globe
- Day traders in the US make around $56.2 an hour on average
- 60% of day traders are over 40 years old
Tax Implications for Day Traders in India
In India, the tax man will want his share if you’re making money from day trading. Here’s how it works:
- Short-Term Capital Gains (STCG): If you make money by selling stocks within a year, you pay 15% tax on your profits.
- Business Income: If day trading is your main job, your profits could be treated as business income, which means you’d be taxed at the standard rates based on your income slab (up to 30% in higher slabs).
- GST on Brokerage Fees: There’s also 18% GST on brokerage fees and commissions, which can add up if you’re trading frequently.
- Securities Transaction Tax (STT): Every time you buy or sell shares in the Indian stock market, you pay STT. For equity delivery trades, STT is 0.1% on both buy and sell. However, for intraday trading (which most day traders do), STT is only applied on the sell transaction, typically at 0.025%.
It’s always a good idea to consult a tax professional to know how much you’ll owe.
Some of the Day Trading Strategies
- Scalping: This strategy is all about making lots of small profits. Traders using scalping buy and sell quickly, holding their trades for just a few minutes.
- Momentum Trading: Traders using this strategy try to catch stocks that are moving strongly in one direction, either up or down. Once the momentum slows, they sell to lock in their gains.
- Breakout Trading: This strategy looks for stocks that are breaking out of a previous price range. If a stock has been trading between ₹100 and ₹110 for a while, and it suddenly goes above ₹110, traders might buy in, expecting the price to keep rising.
- News Trading: As the name suggests, this strategy involves trading based on news announcements. If a company reports better-than-expected earnings, its stock price may shoot up, and traders jump in to catch the wave.
Final Thoughts
Day trading can be exciting and profitable, but it’s not for everyone. It takes patience, practice, and a strong understanding of the markets. Before jumping in, it’s important to educate yourself and start small.
If you think you’ve got the skills and discipline, who knows? You might be the next day trading hero!