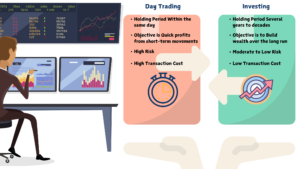
Swing trading is a popular strategy among traders that focuses on capturing short- to medium-term price movements in financial markets.
Unlike day trading, which requires constant monitoring and frequent trades within a single day, swing traders hold positions for several days or weeks, aiming to profit from market swings.
This approach allows traders to take advantage of market trends and reversals while balancing the flexibility of a longer time horizon.
One of the most critical tools in swing trading is earnings reports.
These quarterly updates from companies provide vital information about their financial performance, such as revenue, profit margins, and future projections.
Earnings reports have the power to significantly influence stock prices, often leading to sharp increases or decreases in value.
For swing traders, this volatility offers unique opportunities to capitalize on price movements triggered by surprises in earnings or future guidance.
In this blog, we’ll explore how swing traders use earnings reports to their advantage, leveraging the information they provide to make well-timed and profitable trades during earnings season.
What Are Earnings Reports?
Earnings reports are official financial statements issued by publicly traded companies on a quarterly basis, providing a detailed account of their financial performance over a specific period.
These reports are crucial for investors and traders as they offer insights into a company’s health and its ability to generate profits.
Earnings reports not only reflect past performance but also provide guidance on future expectations, which can impact investor sentiment and stock prices.
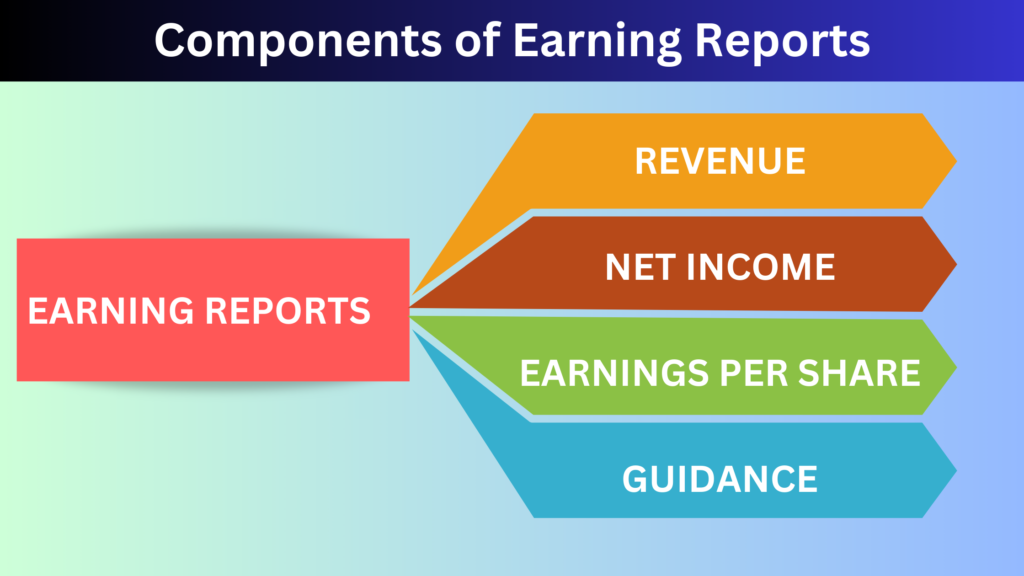
Key Components of Earnings Reports
Revenue: This is the total income generated by the company through its business activities, such as sales or services, before any expenses are deducted. It’s one of the first metrics investors look at to gauge growth.
- Net Income: Also known as profit, net income is what’s left after all expenses (including taxes, interest, and operating costs) are subtracted from the revenue. Positive net income indicates profitability, while negative net income signifies a loss.
- Earnings Per Share (EPS): EPS is a key measure of profitability and is calculated by dividing net income by the number of outstanding shares. It gives investors a clear understanding of how much profit is attributed to each share they own.
- Guidance: Guidance refers to the company’s future outlook, often detailing expectations for revenue, earnings, or growth in upcoming quarters. Forward guidance can have a massive influence on a stock’s price, sometimes even more than the actual earnings figures.
Importance of Quarterly Earnings Reports
Earnings reports are crucial for market participants because they provide real-time insights into a company’s financial performance, helping traders and investors make informed decisions.
These reports often result in significant stock price movements, especially if the company’s performance beats or misses expectations.
Swing traders, in particular, rely on earnings reports to gauge potential volatility and capitalize on price fluctuations.
Why Earnings Reports Matter for Swing Traders
Earnings reports are a critical tool for swing traders because they often result in substantial stock price movements, creating both risk and opportunity.
These reports provide updated insights into a company’s financial health, influencing investor sentiment and leading to significant market reactions.
For swing traders who focus on short- to medium-term price movements, the volatility generated around earnings announcements can offer high-reward trading opportunities.
Key Reasons Earnings Reports Matter for Swing Traders
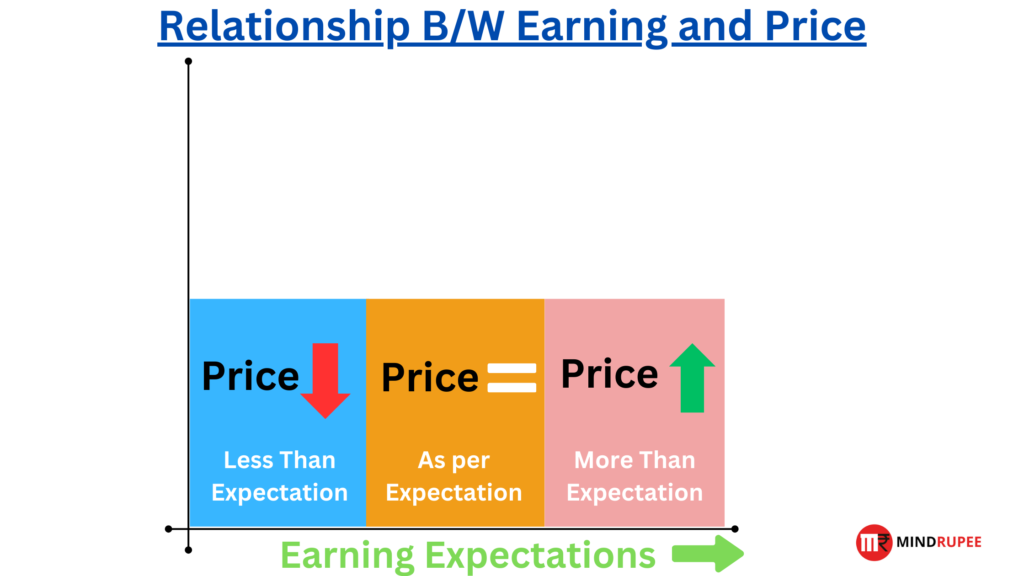
Stock Price Movement
Earnings reports are one of the most common catalysts for stock price fluctuations. If a company exceeds market expectations (a “beat”), its stock price can surge, offering swing traders the chance to capitalize on the upward momentum.
Conversely, disappointing results (a “miss”) can lead to sharp declines, which traders can exploit by shorting the stock or waiting for a buying opportunity.
Volatility Opportunities
Volatility is essential for swing traders, and earnings reports tend to increase market volatility significantly.
This is because earnings reports include not just past performance but also forward guidance, which can surprise the market and shift sentiment dramatically.
Even small discrepancies between expectations and actual results can trigger sharp price movements, ideal for traders looking for quick, profitable swings.
Short-Term Price Movements
The market often reacts swiftly to surprises in earnings or guidance, leading to rapid price changes. Swing traders thrive on such short-term price movements, buying or selling positions within days or weeks.
Earnings reports, especially those that deviate from analysts’ expectations, provide the perfect conditions for quick trades that can yield significant returns.
By anticipating how the market will react to an earnings report, swing traders can position themselves to take advantage of the post-earnings price fluctuations, making earnings season a highly lucrative period for active traders.
Key Metrics Swing Traders Focus On in Earnings Reports
Swing traders closely monitor specific financial metrics in earnings reports to gauge potential price movements and make informed trading decisions.
These metrics help traders assess a company’s financial health, profitability, and future outlook, which are all critical in predicting short-term stock price changes.
1. Earnings per Share (EPS)
- Definition: EPS represents the portion of a company’s profit allocated to each outstanding share of common stock.
- Why It Matters: Swing traders use EPS as a key indicator of a company’s profitability. A company that beats or misses EPS expectations can experience sharp price movements. Positive surprises typically drive stock prices higher, while negative surprises can lead to sell-offs. Swing traders capitalize on this volatility by entering or exiting trades based on the EPS performance relative to market expectations.
2. Revenue Growth
- Definition: Revenue is the total income generated by a company from its operations before any expenses are deducted.
- Why It Matters: Strong revenue growth signals that the company is expanding its market share or product demand is increasing, which is a positive sign for future performance. Swing traders watch revenue trends to assess whether the company is growing at a healthy pace. A significant beat in revenue can trigger a stock price rally, while a miss can lead to declines. Revenue is often a leading indicator of long-term growth, so any surprises can have a significant short-term impact on stock price.
3. Forward Guidance
- Definition: Forward guidance is the company’s projection of future earnings, revenue, and other key performance metrics.
- Why It Matters: Swing traders often pay more attention to forward guidance than actual earnings. Even if a company meets or beats its current earnings, if its forward guidance is weak, the stock may drop as investors adjust their expectations. Conversely, strong forward guidance can lead to price increases as it signals potential growth. Traders use forward guidance to anticipate future trends and decide on trade entry and exit points.
4. Key Financial Ratios and Metrics
- Profit Margins: Swing traders look at profit margins to understand how efficiently the company is managing its costs. Improving margins are a positive sign and can push stock prices higher, while shrinking margins can indicate financial trouble.
- Operating Income: This metric shows the company’s profit from regular business operations. Swing traders monitor operating income to ensure the core business is performing well and contributing to overall profitability. Consistent growth in operating income signals operational efficiency and stability, which can positively affect the stock price.
By focusing on these key metrics, swing traders gain insight into a company’s financial performance and can time their trades around earnings reports to capitalize on price swings.
Earnings Season: The Best Time for Swing Trading Opportunities
Earnings season presents one of the most exciting times for swing traders, offering multiple opportunities to capitalize on short-term volatility.
It is a period when a majority of publicly traded companies release their quarterly earnings reports, and stock prices can react dramatically to the results.
Why Earnings Season is Ideal for Swing Trading?
Earnings season creates frequent price swings, providing swing traders with numerous chances to enter and exit positions based on market reactions. Stocks often experience significant movements — either upward or downward — due to earnings surprises, management guidance, or shifts in market sentiment. These rapid movements align perfectly with swing trading’s focus on short- to medium-term price swings, making it a prime period for profit potential.
Scanning for Stocks Reporting Earnings
Swing traders actively scan for stocks set to report earnings during the season.
By narrowing down a list of potential trades based on upcoming earnings announcements, traders can focus on stocks that are likely to experience heightened volatility.
Swing traders often use earnings calendars or screeners to filter stocks by upcoming earnings dates.
Tools like Screener.in , TradingView, and broker platforms offer detailed earnings schedules, making it easier for traders to plan.
Importance of Planning Trades Around Earnings Events
- Earnings Calendars: Planning trades around earnings events helps swing traders stay organized and prepare for market opportunities. Earnings calendars list the specific dates and times when companies will release their financial reports, allowing traders to strategically position themselves before the release and be ready for potential price movements afterward.
- Volatility Expectation: Swing traders also monitor options prices to gauge the implied volatility (IV) surrounding earnings. Higher IV suggests the market is expecting larger price moves, which could create more significant trading opportunities.
By preparing in advance and using earnings calendars, swing traders can plan their trades around key earnings reports and potentially benefit from the volatility created during earnings season.
How Swing Traders Interpret Earnings Surprises?
Earnings surprises, where actual results differ significantly from analysts’ expectations, often trigger large, immediate price movements. Swing traders take advantage of these surprises, quickly reacting to the market’s response and identifying profitable trade opportunities.
Positive vs. Negative Earnings Surprises
- Positive Earnings Surprises: When a company’s earnings exceed expectations, it often leads to a rapid increase in stock price. Swing traders may take long positions on these stocks, expecting the momentum to carry forward, at least in the short term. Stocks that beat earnings expectations may also see increased buying interest, pushing the price higher, creating ideal conditions for swing traders to ride the upward movement.
- Negative Earnings Surprises: Conversely, when earnings fall short of expectations, the stock price often drops sharply. Swing traders can capitalize on this by shorting the stock, betting that the price will continue to fall as the market reacts negatively to the disappointing results. Some swing traders may also look for buying opportunities after the initial sell-off if they believe the stock is oversold.
Swing Trading Strategies Based on Earnings Surprises
- Buying on Positive Surprises: When a company reports better-than-expected earnings, swing traders look for upward price momentum. The strategy often involves entering the trade shortly after the positive earnings report is released and riding the momentum for a short-term gain. Traders can also set stop-loss orders below support levels to protect against potential reversals.
- Shorting on Negative Surprises: If a company delivers negative earnings surprises, swing traders may short the stock, anticipating further downside pressure. The strategy revolves around catching the downward momentum, with traders setting profit targets or trailing stops to lock in gains as the stock declines.
Using After-Hours and Pre-Market Data
Swing traders often rely on after-hours and pre-market data to make quick decisions following earnings reports. Earnings are typically announced outside of regular trading hours, which means the price reaction occurs in extended trading sessions. By analyzing price and volume action during these periods, swing traders can decide whether to enter or exit trades before the next regular market open.
- After-Hours Data: Many companies release earnings reports after the market closes, and stocks often react immediately in after-hours trading. Swing traders track this data to see how the market is reacting to the earnings surprise, providing clues on how the stock might behave the next day.
- Pre-Market Data: For companies that release earnings in the morning, swing traders monitor pre-market activity to gauge the initial market sentiment. If a stock experiences significant moves in pre-market trading, it can provide valuable insights into how the regular trading session may unfold.
By quickly interpreting earnings surprises and using after-hours or pre-market data, swing traders can take advantage of immediate price movements, either profiting from positive momentum or mitigating losses from negative surprises.
Using Earnings Reports in Swing Trading Strategies
Swing traders employ a variety of strategies to capitalize on the volatility and price movements surrounding earnings reports. These strategies can be categorized into pre-earnings and post-earnings approaches, with some traders focusing specifically on the price gaps that often occur after earnings announcements.
1. Pre-Earnings Strategies
Swing traders often position themselves ahead of earnings reports, anticipating how the market will react to the company’s financial performance. Key factors such as historical earnings performance, analyst expectations, and market sentiment play a critical role in shaping pre-earnings strategies.
- Analyzing Historical Performance: Traders look at how a stock has responded to previous earnings reports. If a stock tends to rally after beating expectations, traders may take a bullish position before the report, hoping for a similar result. Conversely, if a stock consistently drops after missing expectations, traders might consider shorting the stock.
- Assessing Market Sentiment: Leading up to an earnings release, traders monitor news, social media, and analyst reports to gauge the general sentiment around the stock. Positive sentiment may signal that the market expects an earnings beat, while negative sentiment could indicate caution or fear of a miss.
- Risk Management: Since earnings reports can cause significant price volatility, traders often manage risk by sizing their positions carefully, using stop-loss orders, and being prepared for unexpected market reactions.
2. Post-Earnings Strategies
After an earnings report is released, the stock usually experiences an immediate price reaction. Swing traders look for opportunities to profit from the momentum or reversals that follow.
- Buying or Selling After the Release: Swing traders may enter positions based on how the stock reacts to the earnings report. If the report is better than expected, they may buy in anticipation of further gains. If the report disappoints, traders may sell or short the stock, expecting continued downside pressure.
- Focusing on Price Gaps: Price gaps frequently occur after earnings reports, where a stock opens significantly higher or lower than its previous close. Traders may capitalize on these gaps by using a gap trading strategy.
3. Gap Trading
One of the most popular strategies for swing traders around earnings season is gap trading. Price gaps occur when a stock opens at a much higher or lower price than its previous close, often due to the market’s reaction to earnings announcements.
- Types of Gaps:
- Gap Up: When a stock opens higher after strong earnings. Traders may enter long positions, expecting the momentum to carry the price further.
- Gap Down: When a stock opens lower after disappointing earnings. Traders may short the stock or look for a reversal after the initial sell-off.
- Gap Fill: Some swing traders focus on gap fill strategies, where they anticipate that the gap will close and the stock will retrace back to its previous level. For example, if a stock gaps down after earnings, a gap fill strategy would involve buying the stock, expecting it to recover to the pre-gap price.
- Post-Gap Trend: Swing traders also analyze whether the price will continue in the direction of the gap (gap continuation) or reverse after the initial reaction (gap reversal). For instance, a gap-up may continue to rise if there’s strong momentum, while a gap-down may recover quickly if the sell-off was overdone.
By using these strategies, swing traders can leverage earnings reports to their advantage, capitalizing on the volatility and price movements that often follow earnings announcements.
Risks of Trading Around Earnings Reports
While trading around earnings reports can provide lucrative opportunities, it also carries significant risks. It’s important for swing traders to recognize and mitigate these risks to avoid heavy losses.
1. Price Volatility
Earnings reports are often accompanied by sharp price movements, making them highly volatile trading events. While volatility creates opportunities, it also increases the risk of trades moving against you very quickly.
- Example: Even if a company reports strong earnings, stock prices can fall due to other factors, such as lower-than-expected guidance, market sentiment, or broader economic concerns. This can result in a sharp reversal, catching traders off guard.
2. Unexpected Results
No matter how much research and preparation go into a trade, earnings surprises—both positive and negative—are common. A stock can gap up or down significantly at market open, and if a trader is on the wrong side, the losses can be substantial.
- Example: A stock might post better-than-expected earnings but provide weak forward guidance, resulting in a price drop. Conversely, a company could miss earnings expectations but issue strong guidance, causing the stock to rise unexpectedly.
3. Market Overreactions
Sometimes, market participants overreact to earnings reports, leading to extreme price movements that may not align with the company’s fundamentals. These overreactions can result in a price swing in one direction, only to reverse shortly afterward.
4. Importance of Risk Management
Given these risks, swing traders should employ robust risk management strategies, such as:
- Setting Stop-Loss Orders: Always set a stop-loss order to limit potential losses in case of unexpected price movements. This helps protect your capital from sharp downturns following earnings releases.
- Position Sizing: Avoid putting too much capital into a single trade around earnings to reduce the impact of unexpected results.
Combining Earnings Reports with Technical Analysis
To increase their chances of success, swing traders often combine earnings reports with technical analysis to better understand market reactions and predict future price movements.
1. RSI (Relative Strength Index)
The RSI helps traders assess whether a stock is overbought or oversold following an earnings report. After an earnings announcement, an overbought condition could signal that the stock is likely to correct, while an oversold RSI might indicate a potential buying opportunity.
- Example: A stock that gaps down after an earnings miss may hit oversold RSI levels, providing an opportunity for a swing trader to go long, expecting a rebound.
2. MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)
Swing traders can use the MACD to identify shifts in momentum after an earnings report. A bullish MACD crossover following strong earnings may confirm upward momentum, while a bearish crossover after a miss can indicate further downside.
- Example: If the MACD lines cross upward after positive earnings, it signals potential for a continuation of the rally, giving swing traders a confirmation to enter long positions.
3. Moving Averages
Moving averages provide additional context to price action after earnings. Traders look for price action around key moving averages (e.g., the 50-day or 200-day moving average) to make informed decisions.
- Example: A stock might gap down below its 50-day moving average after poor earnings, which could serve as a signal for a continued downtrend.
4. Chart Patterns and Volume Analysis
Earnings reports can lead to the formation of chart patterns that provide actionable insights. Combined with volume analysis, these patterns help traders gauge the strength of price moves.
- Breakout or Breakdown: If a stock breaks out of a consolidation range following an earnings report, it signals potential continuation in the direction of the breakout. Higher-than-average volume during the breakout reinforces the strength of the move.
By combining technical indicators with earnings report analysis, swing traders can create a more well-rounded approach to their trades, improving both their timing and decision-making processes.
Best Practices for Swing Trading Earnings Reports
To successfully swing trade around earnings reports, traders need to implement a structured approach that manages risk while capitalizing on potential price movements. Here are some best practices for doing so:
1. Manage Risk with Stop-Loss Orders
Swing trading around earnings reports involves volatility, so it’s critical to protect your capital with stop-loss orders. Place your stop-loss slightly below key support levels or a percentage point based on your risk tolerance to minimize potential losses if the trade moves against you.
- Example: If a stock is expected to react to earnings, consider setting your stop-loss below a significant moving average or Fibonacci retracement level to safeguard against a sharp drop.
2. Plan for Pre- and Post-Earnings Trades
Have a clear plan for entering and exiting trades both before and after earnings reports. This plan should include:
- Pre-Earnings Strategy: Analyze historical trends and expectations to make an informed decision about positioning before the earnings report.
- Post-Earnings Strategy: Monitor price action after earnings to identify price gaps or volatility that can create trade setups.
3. Use Small Position Sizes
Because of the uncertainty surrounding earnings, it’s advisable to reduce the size of your positions to manage risk. Allocate a smaller portion of your capital to earnings trades to limit exposure in case the trade goes wrong.
4. Stay Informed and Up-to-Date
Earnings reports and analysts’ expectations are constantly changing, so it’s important to stay informed. Regularly monitor earnings calendars and use brokerage alerts to keep track of upcoming announcements that could affect your positions.
- Earnings Calendars: Platforms like TradingView and Yahoo Finance offer easy-to-access earnings calendars to help you prepare for upcoming reports.
5. Avoid Holding Through Earnings if Unsure
Sometimes, the risk of holding a position through an earnings announcement is too great. If you’re uncertain about how the market will react, consider closing the trade before the announcement to avoid potential losses.
6. Watch After-Hours and Pre-Market Activity
After-hours and pre-market trading sessions often show the first signs of market reaction to earnings reports. Keep an eye on these sessions to gain insight into how the market may react when regular trading opens.
7. Be Ready to Act Quickly
Earnings reports can cause quick and decisive movements, so be prepared to act quickly. Set alerts or use automated orders to enter or exit trades swiftly in response to earnings surprises.
Conclusion
Earnings reports are a powerful tool for swing traders, offering opportunities to profit from price volatility and market reactions. By analyzing key metrics such as EPS, revenue growth, and forward guidance, swing traders can identify potential trading setups around earnings season.
However, trading around earnings comes with risks. Therefore, it’s essential to combine earnings report analysis with technical indicators like RSI, MACD, and moving averages to confirm trends, manage risk, and avoid emotional decision-making. Whether you are implementing a pre-earnings or post-earnings strategy, discipline and risk management are key to ensuring long-term success.
Swing traders who successfully integrate earnings report analysis into their broader trading strategy stand a better chance of capturing profitable trades while navigating the volatility that often accompanies earnings announcements. Keep learning, practicing, and refining your approach to make the most of this essential swing trading tool.