Imagine entering the world of swing trading with charts showing endless time frames, each offering a different view of price action.
Where Do we Start?
what is the best time frame for Swing Trading ? All these questions would cloud our mind.
Choosing the right time frame can make or break your strategy in swing trading.
Swing trading is about capturing medium-term price movements, holding positions for a few days to weeks. The choice of time frame is crucial, as it directly influences your strategy’s success.
In this blog, we will explore the most popular time frames for swing trading and help you find the one that fits your trading style.
1. What Are Time Frames in Trading?
Before we go to Time Frame we need to understand Candlestick.
A candlestick chart is one of the most popular types of charts used in trading because it visually shows the high, low, open, and close prices for each time period, making it easier to identify market trends and potential reversal points. Each candlestick represents the price movement of an asset over a selected time frame. It is also called as Japanese Candlestick.
For example:
- In a 1-hour time frame, each candlestick represents one hour of price action.
- In a 4-hour time frame, each candlestick represents four hours of price action.
- In a daily time frame, one candlestick summarizes an entire day’s trading activity, showing the opening price, closing price, and the highest and lowest points during that day.
- In a Weekly time frame, one candlestick summarizes an entire Week’s trading activity, showing the opening price, closing price, and the highest and lowest points during that Week.
Candlesticks provide a visual representation of market sentiment during the chosen time frame.
A green candlestick (or a white one in some chart settings) shows that the price closed higher than it opened, indicating bullish sentiment, while a red (or black) candlestick indicates bearish sentiment where the price closed lower than it opened.
Now coming back to Time Frame!!
In trading, a time frame refers to the specific period during which price movements of a financial asset, like a stock or currency, are recorded and represented on technical charts.
Different time frames display the price action over varying durations, such as 1 minute, 5 minutes, 1 hour, 4 hours, a day, or even a week.
These time frames allow traders to analyze price trends and patterns based on how the market behaves over that period.
For example, in a daily time frame, each price bar or candlestick represents one day of price movement. Traders select time frames based on their trading strategies, with longer time frames typically suited for long-term investors and shorter time frames favored by day traders and swing traders.
- Definition: Explain what a time frame means in the context of technical charts (e.g., daily, hourly, weekly time frames).
- Candlestick Representation: Introduce candlestick charts and explain how each candlestick represents a time frame (e.g., 1-hour chart means one candle equals one hour of price movement).
- Importance of Choosing the Right Time Frame: A wrong time frame can lead to poor decisions—too short and you’ll deal with noise; too long and you might miss important market shifts.
Example:
If you’re trading on a 15-minute chart, you’re likely to deal with unnecessary noise. On the other hand, a weekly chart might miss out on the detailed movements essential for timely swing trading decisions.
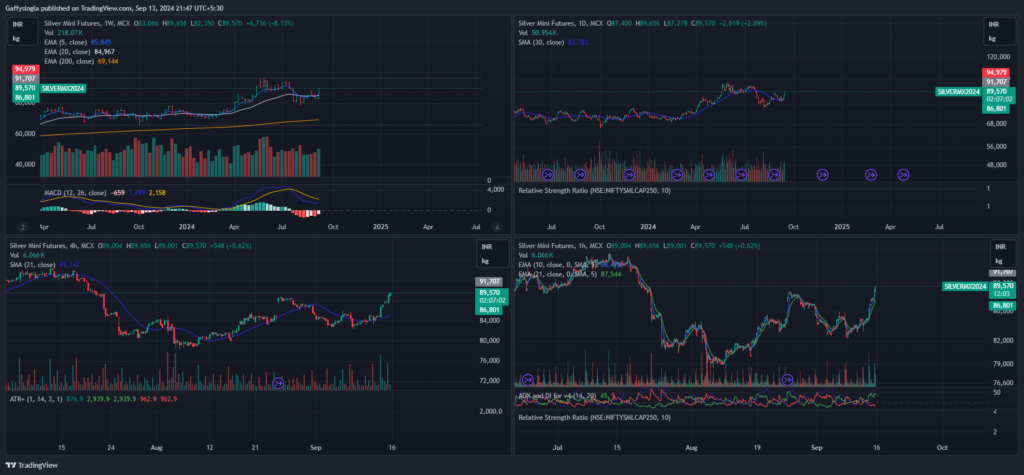
Multiple Tie Frame Example
2. Why Time Frames Matter for Swing Trading?
Swing trading is a popular trading strategy that focuses on capturing medium-term price movements. Unlike day traders who execute multiple trades in a single day or long-term investors who hold positions for months or even years, swing traders aim to capitalize on market swings that occur over several days to weeks.
The goal is to ride the “swings” in price action — both upward (bullish) and downward (bearish) — within the broader trend. This approach allows swing traders to benefit from the natural ebbs and flows of the market without needing to monitor trades constantly, like day traders do.
However, timing is everything in swing trading, and selecting the right time frame is crucial for determining when to enter and exit trades effectively.
Time Frames Influence Strategy
The time frame you choose directly influences your trading strategy, including:
- Entries and exits: The time frame helps you identify the best moments to enter a trade when the price shows a swing or reversal and exit before the momentum changes direction.
- Duration of trades: Longer time frames like daily or weekly charts indicate that you’ll be holding your positions for several days or weeks, while shorter time frames (e.g., 4-hour charts) allow for quicker trades.
- Market perspective: Time frames shape your market view, allowing you to either zoom in on short-term price fluctuations or focus on broader trends over a more extended period.
- Drawdowns : The time frame you choose for swing trading can significantly impact the size and frequency of drawdowns. This is because different time frames expose you to varying levels of market volatility, trend reversals, and price fluctuations, all of which affect how much you lose during a losing trade or streak.
Balance Between Noise and Trend
One of the biggest challenges swing traders face is balancing market noise and the overall trend.
Noise refers to short-term, often insignificant price fluctuations that don’t reflect the broader market direction.
If you’re too focused on short time frames, you risk being misled by these minor movements, which can cause poor decision-making.
- Shorter time frames (like the 1-hour or 4-hour charts or below) provide more granular detail, allowing traders to see minor price movements. However, they also introduce a lot of noise. For example, on a 1-hour chart, small, temporary price spikes could be interpreted as a potential trend reversal, leading traders to enter or exit trades prematurely. Additionally, shorter time frames require more attention and constant monitoring to avoid being caught off guard by small market fluctuations.
- Longer time frames (like daily or weekly charts) smooth out this noise and provide a clearer picture of the overall trend. They focus on price movements that matter and show whether the market is trending upward, downward, or sideways over a more extended period. These longer time frames are particularly useful for swing traders who want to capture significant price swings without being distracted by minor, temporary fluctuations.
Example
Let’s say you’re analyzing a stock to determine if it’s in an upward trend. Using a 15-minute chart, you’ll see every minor fluctuation, including small price pullbacks, which can create confusion and lead to overtrading.
You might see a minor dip in price and assume the trend is reversing when, in fact, it’s just a temporary correction before the price moves higher. This noise can make it harder to see the broader trend, leading to unnecessary trades or missed opportunities.
Now, if you switch to a daily chart, the smaller fluctuations are smoothed out, and you’re left with a clearer view of the stock’s broader price trend. You can now focus on identifying significant swings in price and make better-informed decisions based on the overall market direction. A daily chart would show a more reliable picture of the stock’s upward momentum without being impacted by the minor price corrections seen in the 15-minute chart.
In this scenario, using a daily time frame helps you stay aligned with the larger trend, making it easier to spot the right time to enter and exit the trade, without being distracted by irrelevant short-term noise.
3. Best Time Frames for Swing Trading
Selecting the right time frame is a critical decision for swing traders. The chosen time frame determines how much noise you’re exposed to, how much time you spend monitoring the market, and how often you make trades. Each time frame offers a unique balance of advantages and disadvantages, depending on your trading style, availability, and objectives. Let’s break down the best time frames for swing trading:
- 1-Hour Chart:
- Pros:
- Intraday Insights: The 1-hour chart provides a detailed view of price movements throughout the day, helping you spot multiple entry and exit points within a trading session.
- Balanced Noise Level: It strikes a balance by offering enough price data to show meaningful trends without the extreme noise of shorter time frames like the 5-minute or 15-minute charts.
- Frequent Opportunities: The 1-hour chart offers more frequent trade setups, making it ideal for traders who enjoy being actively engaged with the market but don’t want to over-trade.
- Cons:
- Requires Constant Monitoring: To effectively use a 1-hour chart, traders need to check their charts multiple times a day. Missing a key moment could lead to missed opportunities or poor trade execution.
- Higher Risk of Overtrading: The constant access to new price data could tempt traders into making too many trades, increasing exposure to potential losses.
- Best for:
- Traders who are comfortable checking charts several times throughout the day but still want enough time between trades to make thoughtful decisions.
- Ideal for those who want to catch intraday trends while avoiding the minute-by-minute chaos of lower time frames.
- Example: You spot a potential breakout forming in a stock, and the 1-hour chart allows you to see how price reacts during intraday highs and lows, giving you an opportunity to make a well-timed trade without the noise of shorter time frames.
- Pros:
- 4-Hour Chart:
- Pros:
- Balanced View: The 4-hour chart offers a great balance between short-term and medium-term trading. It allows you to observe trends as they develop throughout the trading day, providing more refined signals than daily charts without the need for constant monitoring.
- Captures Significant Swings: This time frame is ideal for catching meaningful price swings while filtering out the market noise associated with smaller, less significant price fluctuations.
- Less Time-Intensive: You can analyze and make decisions at regular intervals (e.g., every 4 hours) instead of constantly monitoring the market.
- Cons:
- May Miss Short-Term Opportunities: If the market experiences a rapid change during the day, such as news announcements or sudden volatility, the 4-hour chart might miss out on short-term opportunities that a 1-hour or shorter time frame would catch.
- Less Frequent Setups: You might find fewer trading opportunities compared to using smaller time frames, requiring more patience.
- Best for:
- Traders who don’t have the time to check charts constantly but want more insight than what a daily chart provides.
- Perfect for those who prefer to manage trades during set periods throughout the day.
- Example: If you prefer not to check the market every hour, the 4-hour chart allows you to identify trends forming over a few days while checking your charts just a few times during the trading day. You can catch solid swings without having to micromanage trades.
- Pros:
- Daily Chart:
- Pros:
- Comprehensive View: The daily chart offers a bird’s-eye view of the market, allowing you to focus on broader trends. This time frame smooths out the short-term noise, making it easier to spot trend reversals, support and resistance levels, and key breakouts.
- Less Stress: With fewer data points, the daily chart minimizes over-analysis and allows for more relaxed trading. You don’t need to check your charts frequently, making it less time-consuming.
- Longer Trend Signals: Since you’re focusing on the bigger picture, the daily chart tends to provide stronger and more reliable trend signals, helping you avoid the false signals of lower time frames.
- Cons:
- Misses Short-Term Opportunities: If the market experiences a sharp but short-lived price movement, the daily chart may not capture these movements, leading you to miss potentially profitable opportunities.
- Slower Entries and Exits: Because the daily chart operates over a larger time horizon, your entry and exit signals may come later than on shorter time frames, potentially missing the initial momentum.
- Best for:
- Traders who prefer a more laid-back approach, with fewer trades to manage and monitor.
- Those who focus on major price trends and don’t want to deal with the intraday fluctuations.
- Example: By focusing on the daily chart, you’re able to identify strong bullish or bearish trends over several weeks. You may miss some short-term volatility, but the focus on larger swings helps you capture more significant moves with less screen time.
- Pros:
- Weekly Chart:
- Pros:
- Captures Long-Term Trends: The weekly chart is excellent for spotting major, long-term trends in the market. You can get a clear view of market sentiment over months or years.
- Minimizes Market Noise: Weekly charts are the least affected by minor fluctuations and market noise, making it easier to identify the general direction of a trend without being distracted by daily volatility.
- Low Time Commitment: Weekly charts are perfect for traders who prefer to make long-term decisions without having to check their charts frequently. You can focus on making strategic decisions once a week, minimizing stress and time spent analyzing.
- Cons:
- Slow to React: Because weekly charts are designed for long-term trading, they tend to lag behind shorter time frames. You might not catch quick market reversals, and your trades could be delayed in response to significant events.
- Fewer Trading Opportunities: The weekly chart generates far fewer trade setups compared to shorter time frames, meaning you may need to hold positions longer, which requires more patience.
- Best for:
- Traders who are interested in long-term trends and are looking for fewer but more significant trades.
- Swing traders who are comfortable holding positions for weeks or months and are not concerned with short-term price movements.
- Example: If you are following a long-term trend in the stock market, the weekly chart will help you identify broader market shifts, like the beginning of a new bullish or bearish phase. You can manage trades over several weeks, making decisions based on big-picture analysis.
- Pros:
4. Daily Charts: The Swing Trader’s Best Friend
When it comes to swing trading, daily charts are often considered the ideal tool for many traders.
Why?
Because they strike a perfect balance between providing enough information to make informed decisions while filtering out the short-term noise that can distract and confuse traders on lower time frames.
Let’s dive deeper into why daily charts are the swing trader’s best friend and how they offer unique advantages that make trading easier, more efficient, and less stressful.
Why Daily Charts Work for Swing Traders
Spotting Larger Trends
One of the key reasons daily charts are so effective for swing traders is their ability to clearly display larger price trends. Swing traders aim to capture medium-term price movements that last several days to a few weeks, and daily charts are perfect for this purpose. Unlike the rapid fluctuations seen on shorter time frames like the 1-hour or 15-minute charts, daily charts focus on the broader price movement. This makes it easier for traders to spot significant trends, such as breakouts, reversals, or consolidations, and make decisions based on the bigger picture rather than getting lost in short-term noise.
Better Context for Decision-Making
Since each candlestick on a daily chart represents an entire trading day, traders get a comprehensive look at the day’s market sentiment, including the open, close, high, and low prices. This information is crucial for understanding the market’s overall direction and helps swing traders place trades that are in line with the prevailing trend, increasing the likelihood of success.
Reduced Noise for Better Clarity
Filtering Out Random Movements
In swing trading, unnecessary “noise” refers to the small, random price fluctuations that can lead to false signals or poorly timed trades. These random movements are particularly prevalent in shorter time frames, such as the 15-minute or 1-hour charts, where minor price fluctuations can make it difficult to determine whether a trend is forming or fading. Daily charts, on the other hand, smooth out this noise and focus on the most significant price movements of the day. This gives swing traders a clearer, more reliable view of the market’s overall direction, allowing them to make decisions based on meaningful trends rather than reacting to short-term fluctuations.
Avoiding Overtrading
By eliminating much of the noise present in lower time frames, daily charts also help traders avoid overtrading—a common pitfall where traders place too many trades based on minor price movements. Overtrading can lead to higher transaction costs and more losses due to impulsive decisions. With daily charts, traders are less likely to be tempted by every minor fluctuation, and instead, they can focus on the bigger, more profitable moves.
Lower Transaction Costs
Fewer Trades, Lower Costs
Since swing traders typically hold positions for several days, they naturally make fewer trades than day traders who might execute multiple trades within a single session. Daily charts encourage this slower, more deliberate trading style. Fewer trades mean lower transaction costs, including brokerage fees and spreads. This reduction in trading frequency not only saves money but also reduces the psychological pressure of constantly monitoring the market and making decisions.
Maximizing Profit Potential
By holding positions over a longer period, traders can capitalize on larger price movements. Daily charts help identify these moves, allowing traders to ride trends over multiple days and capture more substantial profits. The slower pace of daily chart trading ensures that traders don’t miss out on big opportunities by prematurely entering or exiting a trade due to short-term market jitters.
Less Time-Consuming
Efficient Market Monitoring
One of the biggest advantages of using daily charts for swing trading is the reduced time commitment. Traders using shorter time frames like the 1-hour or 4-hour charts often need to monitor the market regularly throughout the day to catch every move. This can be time-consuming and stressful. With daily charts, traders can spend just a few minutes each day reviewing the previous day’s price action, identifying key trends or setups, and planning their trades for the coming days. This allows for more flexibility and frees up time for other activities, whether it’s other work, personal hobbies, or simply enjoying more leisure time.
Strategic Decision-Making
Because daily charts provide a more comprehensive view of price trends, traders don’t need to rush their decisions. They have the luxury of taking their time to analyze the market, consider multiple factors, and execute trades with greater confidence. This methodical approach reduces the likelihood of emotional trading—where traders make impulsive decisions based on fear or greed—and increases the probability of making sound, well-considered trades.
5. Why 4-Hour Charts are Also Popular
The 4-hour chart has gained a reputation as one of the most practical time frames for swing traders who want a balance between catching trends and managing their time efficiently. It offers a middle ground between the fast-paced action of lower time frames like the 1-hour chart and the broader, slower movements of the daily chart. Here’s why the 4-hour chart is a favorite among many swing traders and how it fits into various trading styles.
Key Benefits are :
- Less Noise than Lower Time Frames: Compared to charts like the 1-hour or 15-minute time frames, the 4-hour chart filters out much of the short-term volatility and noise, providing clearer signals for trend identification and market direction.
- Quicker Than Daily Charts: While daily charts give a broader view, they can be slower to react to emerging trends. The 4-hour chart, by contrast, allows traders to catch trends and reversals sooner, making it a great option for those looking for a bit more action without constant monitoring.
- More Frequent Setups: The 4-hour chart gives traders access to more trading signals throughout the week, allowing for increased trading frequency. This is particularly advantageous for traders who want more action but still prefer to avoid over-trading, a common issue in lower time frames.
- Better for Capturing Smaller Swings: Swing traders who use the 4-hour chart can target smaller, more frequent price swings, which can add up to significant gains over time. This makes it ideal for traders who want to capture both the medium-term trends and the smaller price fluctuations within those trends.
This time frame strikes a good balance between waiting for the right setup and getting frequent trading opportunities, making it an excellent option for traders who enjoy being active but don’t want to trade constantly.
6. The Role of Multiple Time Frame Analysis
Multiple time frame analysis is a powerful tool for swing traders that involves using more than one time frame to make informed trading decisions. By analyzing charts across different time frames, traders can gain a clearer picture of the market, improve their entry and exit points, and reduce the risk of making trades based on incomplete information. Let’s dive deeper into how this approach works and why it’s so effective for swing traders.
Using Multiple Time Frames Together
Swing traders typically focus on one primary time frame for making decisions, such as the daily or 4-hour chart. However, combining a higher time frame (like daily or weekly charts) with a lower time frame (such as 1-hour or 4-hour charts) helps to fine-tune trade entries and exits. This is because higher time frames provide a broader perspective on market trends, while lower time frames offer more granular details about price movements.
- Higher Time Frame for Trend Identification: The higher time frame (e.g., daily or weekly) helps traders identify the general direction of the market. Is it trending up, down, or moving sideways? This broader view helps traders align their trades with the dominant market direction, avoiding potential losses from trading against the trend.
- Lower Time Frame for Precise Entries and Exits: After confirming the overall trend, traders can switch to a lower time frame (e.g., 1-hour or 4-hour chart) to time their entries and exits more precisely. This gives them a chance to capture better opportunities within the broader market context.
Trend Confirmation Across Time Frames
Using multiple time frames helps swing traders confirm the strength and direction of a trend. For example, you can check the daily chart to get a sense of the overall market direction and then look at the 1-hour or 4-hour chart to find more detailed patterns that help you make well-timed trades.
- Identifying Major Trends: If the daily chart shows a clear uptrend, it suggests that the market is moving upward. You can then use the lower time frame to spot corrections or retracements within that trend. These smaller pullbacks in an uptrend provide ideal entry points to buy into the trend.
- Avoiding False Signals: Sometimes, a lower time frame may show what looks like a good trade setup, but the higher time frame might reveal a different picture. By using both time frames together, you reduce the risk of entering trades based on false signals or temporary market fluctuations that don’t align with the broader trend.
Finding the Best Setup
Aligning signals across multiple time frames increases a trader’s confidence in a trade setup. For example, if the daily chart shows a bullish trend and the 4-hour chart indicates a short-term pullback, this could be an excellent opportunity to enter a long position. However, if both the daily and 4-hour charts show conflicting signals, it might be a sign to wait for a better setup.
- Entry Points: Once the higher time frame has confirmed the trend, the lower time frame can help traders pinpoint the best entry point. For example, if the daily chart shows an uptrend but the 1-hour chart shows a temporary dip, this could be the perfect moment to enter the trade before the uptrend resumes.
- Exit Points: Similarly, traders can use multiple time frames to decide when to exit. If the higher time frame still supports the trade, but the lower time frame shows weakening momentum, it may be a good time to exit the trade and lock in profits before a reversal.
Example: Combining Daily and 4-Hour Charts for Swing Trading
Let’s consider an example where a swing trader named Rajesh is trading a stock that shows an overall upward trend. Rajesh uses the daily chart to identify the trend, which confirms that the stock is in a solid uptrend. Now, he waits for a better entry point.
- Daily Chart (Higher Time Frame): Rajesh sees that the stock has been trending upward for the past few weeks, confirming that the market sentiment is bullish. He wants to avoid entering the trade when the stock is overbought, so he looks for a pullback in the price.
- 4-Hour Chart (Lower Time Frame): On the 4-hour chart, Rajesh notices a short-term price dip within the larger uptrend. The price pulls back to a key support level, and the RSI (Relative Strength Index) shows the stock is now in an oversold condition, indicating a good time to buy.
By aligning the signals from both the daily and 4-hour charts, Rajesh gains more confidence in his trade setup. The higher time frame shows that the overall trend is up, and the lower time frame confirms a short-term pullback, offering him a better entry point.
Benefits of Multiple Time Frame Analysis
- Improved Precision: By switching between time frames, traders can fine-tune their entries and exits, ensuring they enter trades at the right moment and exit before trends reverse.
- Better Risk Management: The broader perspective from the higher time frame helps traders avoid entering trades during periods of uncertainty, while the lower time frame reduces the risk of missing the best entry point.
- Increased Confidence: When multiple time frames align and confirm each other, traders feel more confident in their trading decisions, reducing hesitation and emotional interference.
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing a Time Frame
Selecting the right time frame is crucial for any trading strategy, especially in swing trading, where you’re holding positions for several days or weeks. Many traders make the mistake of choosing a time frame that doesn’t align with their strategy, leading to suboptimal results. Let’s look at some of the common pitfalls and how they can impact your trading performance.
Choosing Too Short a Time Frame
Using a time frame that is too short, such as a 1-minute or 5-minute chart, can lead to over-trading and reacting to minor price fluctuations. While shorter time frames offer more data points, they can also introduce significant “market noise”—random price movements that don’t reflect the overall market trend. This noise can cause traders to make hasty decisions, often leading to over-trading, increased transaction costs, and emotional burnout.
- Example: A swing trader using a 5-minute chart might see multiple small price movements and interpret them as trade opportunities. However, these fluctuations are often insignificant in the broader market context, causing the trader to enter and exit positions too frequently. This not only results in higher transaction fees but also distracts from the larger price trends that are more important in swing trading.
Solution: Stick to time frames that align with swing trading principles, such as the 1-hour, 4-hour, or daily charts. These time frames help filter out noise and focus on the overall trend, reducing the temptation to trade every minor fluctuation.
Not Aligning the Time Frame with Your Strategy
Your time frame should reflect your overall trading strategy and goals. If you’re a swing trader, you aim to capture price movements over several days or weeks. Using time frames that are suited for day trading, such as 1-minute or 15-minute charts, can lead to mismatches in strategy, where you might start trading based on short-term signals that don’t align with your medium-term goals.
- Example: A swing trader relying on a 15-minute chart may enter trades based on short-term momentum, only to realize later that the larger trend on the daily chart was moving in the opposite direction. This mismatch can lead to entering trades too early or exiting too soon, preventing the trader from capturing the full potential of a swing trade.
Solution: Use time frames that align with the duration of your trades. For swing traders, the 1-hour, 4-hour, and daily charts offer a more appropriate view of the market. These time frames reflect the price movements over the days or weeks you plan to hold your position, making them more suitable for your strategy.
Ignoring Higher Time Frames
Neglecting higher time frames, such as the daily or weekly charts, can result in missing the broader market trend and entering trades that go against the prevailing momentum. Even if you’re using a lower time frame like the 1-hour or 4-hour chart to fine-tune your entries, you should always check the higher time frame to ensure that your trades align with the larger trend.
- Example: A trader using only a 1-hour chart may see a bullish signal and enter a long position, not realizing that the daily chart shows a strong downtrend. As a result, the trader is going against the larger market movement, increasing the risk of a losing trade.
Solution: Always consult higher time frames to understand the broader market context. If the daily or weekly chart shows a clear uptrend, look for long opportunities on the lower time frames. Conversely, if the higher time frame indicates a downtrend, it’s better to seek short positions or stay out of the market.
8. Conclusion: What’s the Best Time Frame for Swing Trading?
For most swing traders, the daily chart is the optimal time frame. It strikes the perfect balance between clarity, trend identification, and time efficiency. The daily chart allows traders to capture meaningful price movements over several days without being bogged down by the market noise that often appears in shorter time frames. Its clarity helps you stay aligned with the broader market trend, making it easier to identify key support and resistance levels, as well as important swing highs and lows.
However, if you’re looking to fine-tune your entries and exits, combining the daily chart with shorter time frames like the 4-hour chart can enhance your trading strategy. While the daily chart provides the overall trend, the 4-hour chart can offer more precise entry points, allowing you to capture market reversals or short-term price movements within the broader trend.
Your Best Time Frame
The ideal time frame for swing trading ultimately depends on your trading style, goals, and the time you can dedicate to monitoring the markets. Swing trading is inherently flexible, so what works for one trader may not work for another. Here’s how to determine the best time frame for you:
- Trading Style: Are you a more conservative trader who prefers to hold positions for a longer period, or do you like more frequent trading opportunities? For those looking for longer trends and less frequent trades, the daily or weekly charts are ideal. If you’re more active and want to catch shorter trends within a day or two, the 4-hour chart may suit you better.
- Goals: Are you aiming for short-term profits, or are you building positions for longer-term gains? Your goals will impact whether you choose a shorter or longer time frame.
- Available Time: If you have limited time to monitor the market, a daily chart is more suitable since it requires less frequent analysis. On the other hand, if you can check the markets several times a day, you might prefer shorter time frames like the 1-hour or 4-hour chart.
Ultimately, the key to successful swing trading lies in finding the time frame that fits your personality and lifestyle. Test different time frames in a demo or live trading environment, and see which one aligns best with your strategy and availability. By choosing the right time frame and combining it with effective trading strategies, you’ll improve your chances of capturing profitable swing trades and achieving consistent success in the markets.