Who are the top 5 quantitative traders in the world, and what makes them excel in such a complex field? This concise overview introduces you to the trailblazers whose data-driven decisions have remarkably influenced trading tactics across the globe. Dive into the details of their innovative strategies and monumental impacts on financial markets without hyperbole or sales pitches.
Key Takeaways
- Quantitative trading is led by elite traders and firms using mathematical and statistical models to capitalize on market opportunities, with renowned figures like Jim Simons, David E. Shaw, and others at the helm.
- Advanced strategies employed in quantitative trading include employing statistical arbitrage, leveraging unconventional alternative data, and incorporating technologies like AI and machine learning to improve trading efficiency and adaptability.
- Quantitative trading significantly affects financial markets by enhancing market liquidity, narrowing bid-ask spreads, lowering transaction costs, and contributing to the price discovery mechanism, despite potential volatility and challenges in dealing with irrational market behaviors.
The Powerhouses of Quant Trading
The thriving world of quantitative trading is dominated by a select group of individuals and firms known for their expertise and groundbreaking contributions in the field. These individuals have transformed the industry, building powerful quant hedge funds and trading firms that leverage mathematical and statistical models to identify trading opportunities in the stock market.
Let’s delve into the stories of these industry titans.
Jim Simons (Renaissance Technologies)

James Simons, a mathematician turned quant trader, is the founder of Renaissance Technologies, a pioneering quantitative trading firm. Founded in 1982, Renaissance Technologies has achieved legendary status within the industry, particularly due to the success of its Medallion Fund.
The Medallion Fund, known for its black-box strategy, manages about $10 billion in financial instruments, including fixed income, and is exclusive to Renaissance’s owners and employees, highlighting the success of Simons’ innovative approach to quantitative trading.
David E. Shaw (D.E. Shaw & Co.)

David E. Shaw is another titan in the world of quantitative trading. His firm, D.E. Shaw & Co., has significantly influenced the evolution of quant trading since its inception, employing innovative strategies and rigorous research to achieve remarkable success in the industry. Shaw’s trailblazing role in the field has paved the way for future generations of quant traders and continues to shape the landscape of the industry.
John Overdeck and David Siegel (Two Sigma)
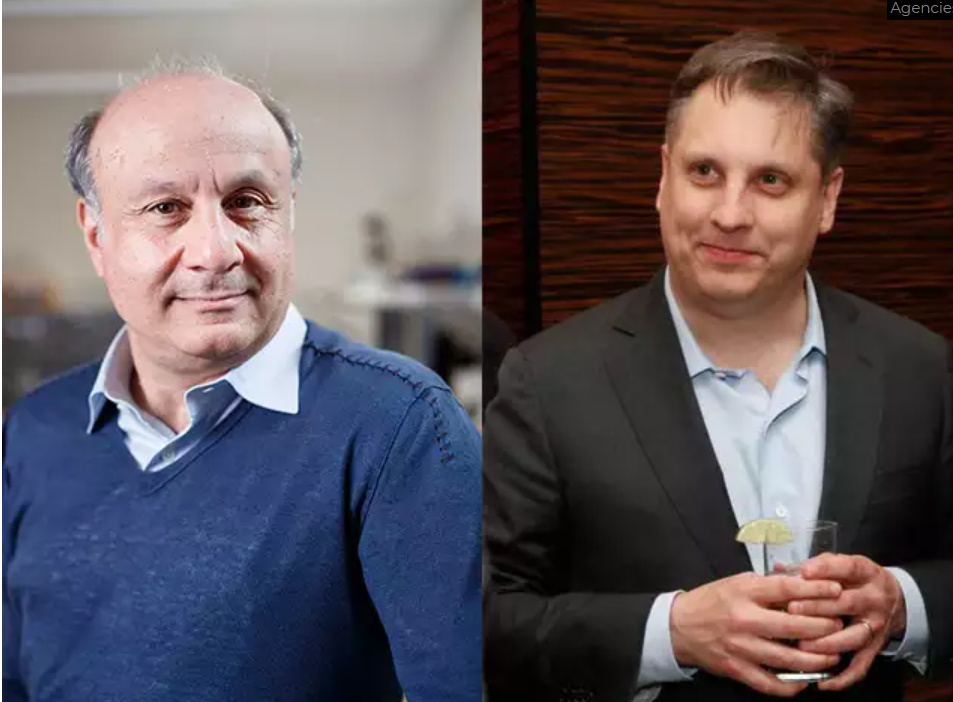

Co-founded by John Overdeck and David Siegel in 2001, Two Sigma is a leading force in the quantitative trading world. With a robust team and billions of dollars under management, Two Sigma has become a beacon of success in the industry.
Through their focus on technology, data analysis, and research, Overdeck and Siegel have built a firm that remains at the forefront of quantitative trading.
Cliff Asness (AQR Capital Management)
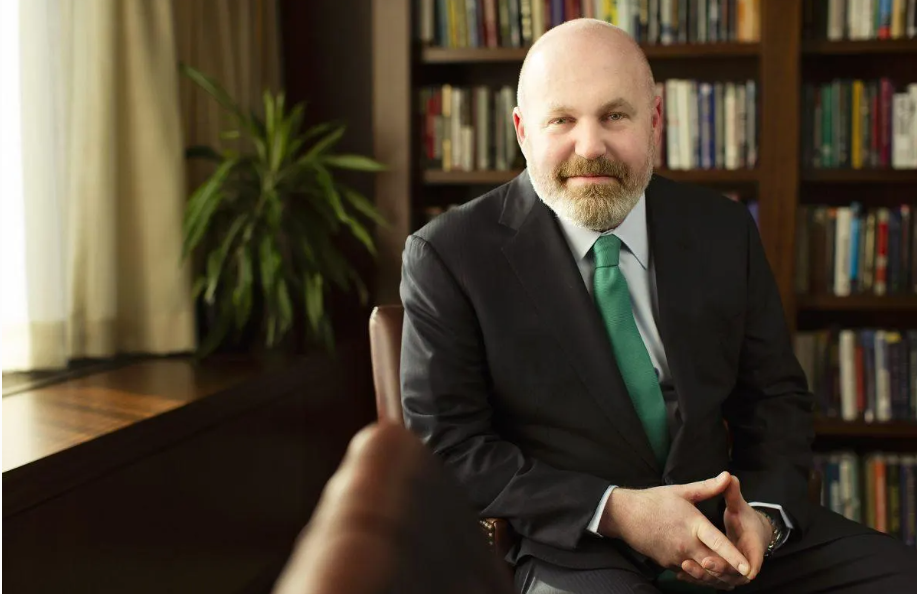

In the realm of quantitative trading, Cliff Asness stands out as a prominent figure. As the co-founder of AQR Capital Management, Asness has championed a scientific approach to investing, integrating academic research into the asset management industry. Under Asness’s leadership, AQR has had a profound impact on the industry, publishing numerous research papers on topics ranging from market anomalies to portfolio optimization, influencing investment strategies across the globe.
Asness’s work has:
- Reshaped how investors manage portfolios across various asset classes
- Had a profound impact on risk management
- Promoted a deeper understanding of how to construct more resilient investment portfolios
- Revolutionized the industry by demonstrating the power and potential of quantitative trading
His contributions to the development of systematic investing approaches have had a significant impact.
Peter Muller (PDT Partners)
Peter Muller, the founder of PDT Partners, is known for his significant contributions to algorithmic trading. Through his leadership, PDT Partners has thrived in the competitive world of quantitative trading, specializing in developing proprietary statistical models designed to accurately predict market movements and profit from them.
Muller’s approach to quant trading is unique, as it involves identifying non-random patterns in various financial markets and exploiting them for generating alpha. His firm, PDT Partners, has earned a reputation for its meticulous research and the effective application of statistical analysis in its trading algorithms.
Muller’s integration of advanced machine learning techniques to distill and capitalize on complex market data represents the forward-thinking approach adopted by the leading quant traders of today.
Strategies Employed by Top Quant Traders
Top quantitative traders employ a variety of strategies, meticulously crafted using mathematical and statistical techniques such as time series analysis, regression models, and machine learning algorithms. Among these strategies, statistical arbitrage stands as a key approach, employing the concept of mean reversion to capitalize on substantial divergences from calculated averages in the price relationships between a group of assets.
Beyond traditional methods, quantitative trading firms are increasingly harnessing unconventional alternative data sources to extract market insights and gain a competitive edge. These sources include satellite imagery, social media, and internet search data. Momentum investing and trend following are also prominent quantitative strategies, where quant traders analyze longer-term price movements to discern market trends. The goal is to purchase assets that are increasing in value, aiming to sell them near their peak, thus optimizing returns. In this process, quant analysts play a crucial role in developing and implementing these strategies.
Impact on Financial Markets
The impact of quantitative trading on financial markets is profound. It enhances market liquidity, smoothing out high demand impacts and promoting accurate asset pricing. The technological advancements brought about by quantitative traders have resulted in increased market liquidity, narrower bid-ask spreads, and lower transaction costs.
Beyond trade execution, quantitative trading also plays a significant role in the price discovery mechanism, influencing the interplay of various trader behaviors. However, it’s important to note that despite these advantages, quantitative trading can introduce market volatility and faces challenges in adapting to the irrational behavior patterns of human investors.
Skillsets and Education of Top Quant Traders
Successful quant traders typically possess a unique blend of skills and educational backgrounds. These individuals often hold at least a bachelor’s degree in areas such as mathematics, statistics, finance, or computer science. Many top quant traders go further, obtaining higher academic qualifications like a master’s degree in mathematical finance or a Ph.D. in quantitative disciplines. These advanced degrees are often preferred for top quant trader roles, reflecting the rigorous intellectual demands of this field.
Alongside their strong academic backgrounds, successful quant traders need robust programming skills, particularly in languages like Python, R, C++, or MATLAB. However, beyond their technical abilities, these traders must also excel in soft skills. This includes coping with stress, adjusting to market shifts, and effective risk management. These skills are essential for navigating the rapid changes and high-pressure environment of quantitative trading.
The Future of Quantitative Trading
As we look to the future, the incorporation of AI and machine learning in quantitative trading promises to bring significant improvements and advancements to the field. AI has significantly enhanced the capabilities of quantitative trading firms, enabling them to analyze vast amounts of data and identify complex patterns with unprecedented efficiency. As AI technologies continue to advance, the quantitative trading landscape is expected to see further innovations and advancements. This will likely have significant impacts on the financial markets..
The utilization of AI is anticipated to bring significant improvements to individual aspects of the investment process, including forecasting, modeling, and execution. Large datasets can now be processed and analyzed through machine learning and statistical modeling, enhancing the complexity and effectiveness of trading strategies. With the incorporation of AI and machine learning into quantitative trading, strategies can adapt more effectively to market changes, offering a promising outlook for the future of the industry.
Tips for Aspiring Quant Traders
For those aspiring to join the ranks of top quant traders, here are some key steps to take:
- Hone a strong foundation in math, probability, and statistics, as these topics often form the basis for interview questions at quant funds.
- Enhance coding skills, particularly for those aiming for Trader or Developer roles at quant funds.
- Showcase your interest in financial markets through relevant side projects or internships.
- Network with industry professionals to gain valuable insights and potential job opportunities.
By following these steps, you can increase your chances of success in the world of quant trading.
Lastly, remember to ensure a refined resume, cover letter, and a portfolio showcasing relevant experience and achievements when applying for a quant trading career.
Challenges Faced by Quant Traders
While the world of quant trading offers immense potential, it also presents its own set of challenges. Technological failures, such as connectivity and power outages, can disrupt quant trading systems and operations, impacting the execution of trades. Additionally, periods of high market volatility can introduce heightened uncertainty, particularly when traders have to turn off their trading programs.
Further challenges arise from the complexity of some advanced trading strategies, which can be difficult to effectively translate into code. Even after successful implementation, quant traders face a constant battle to develop new strategies, as market changes can render existing strategies less effective over time. Coding errors in automated trading systems can trigger unintended trades, leading to substantial financial losses, and quant trading is also vulnerable to the risk of curve fitting, where strategies may fail to perform as expected in live trading environments.
The Role of Technology in Quant Trading
Technology plays a pivotal role in the world of quantitative trading, supporting rapid trade execution, advanced risk management, and the processing of vast amounts of real-time data. Algorithmic trading, high-frequency trading, and advanced algorithms enable quant traders to execute a high number of trades swiftly and respond to market conditions with precision. In the realm of risk management, algorithms continuously monitor and adjust trading positions in line with pre-set risk parameters, providing a robust framework for managing potential losses.
Moreover, quant traders:
- Harness algorithmic pattern recognition to uncover hidden institutional trading patterns
- Utilize various analysis software to support their trading decisions
- Use programming languages such as C++, Java, Python, and Perl in conjunction with tools like MATLAB to develop and operate complex trading algorithms
- Process vast amounts of real-time data with the help of artificial intelligence to extract actionable insights and enhance their trading capabilities.
Ethical Considerations in Quantitative Trading
Quantitative trading, like any field, has its ethical considerations. Market manipulation is one such concern, where traders could potentially exploit advanced algorithms to take advantage of market vulnerabilities. In addition, information asymmetry presents ethical challenges, as quant trading relies on safeguarding sensitive financial information while preventing unauthorized access.
Algorithmic bias in quant trading models can perpetuate discrimination if the underlying data reflect existing prejudices, posing significant ethical concerns. Ensuring accurate communication of risks to investors and stakeholders is an ethical obligation for quant traders, aimed at minimizing potential financial harm. Adherence to ethical codes, like those from the CFA Institute, and ongoing ethics education and training are crucial for fostering sound ethical decision-making in the quantitative trading profession.
Summary
In conclusion, the world of quantitative trading is an intricate blend of mathematics, statistics, technology, and financial acumen. The top quantitative traders, like Jim Simons, David E. Shaw, John Overdeck, David Siegel, Cliff Asness, and Peter Muller, have not only achieved remarkable success but have also been instrumental in shaping the industry. Their contributions, coupled with the advancements in technology and AI, have revolutionized trading strategies, enhanced market liquidity, and influenced the price discovery mechanism. However, as the field evolves, it also presents its own set of challenges and ethical considerations, necessitating continuous learning, adaptation, and integrity from those who venture into it.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is quantitative trading?
Quantitative trading is a method that uses advanced mathematical models, algorithms, statistics, computer programming, and financial knowledge to identify trading opportunities in the market.
Who are some top figures in the field of quantitative trading?
Some top figures in the field of quantitative trading are Jim Simons, David E. Shaw, John Overdeck, David Siegel, Cliff Asness, and Peter Muller. These individuals have made significant contributions to the industry.
What are the key strategies employed by quant traders?
Quant traders employ a variety of strategies such as statistical arbitrage, momentum investing, trend following, and alternative data sourcing, all of which are based on mathematical and statistical techniques.
What challenges do quant traders face?
Quant traders face challenges such as technological failures, market volatility, implementing complex strategies, coding errors, and the risk of curve fitting in trading strategies. These challenges require careful consideration and risk management.
What ethical considerations are associated with quantitative trading?
The ethical considerations in quantitative trading include market manipulation, information asymmetry, algorithmic bias, and the need for accurate risk communication and adherence to ethical codes. These are important factors to be mindful of when engaging in quantitative trading.