Swing trading is a dynamic strategy that focuses on capturing gains in a stock (or any financial instrument) over a few days to several weeks.
While many traders primarily rely on technical analysis to spot trading opportunities, incorporating fundamental analysis
can significantly enhance your strategy.
This comprehensive guide will delve deep into how you can effectively combine fundamental analysis with swing trading to boost your success in the markets.
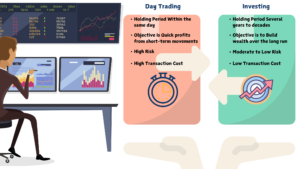
If you want to learn about the difference between swing trading and Day Trading : You can Read Swing Trading Vs. Day Trading : Which Strategy Suits You Best?
What is Fundamental Analysis in Swing Trading?
Fundamental analysis involves evaluating the intrinsic value of a financial asset by analyzing various economic, financial, and qualitative factors.
Unlike technical analysis, which is focused on price movements and patterns, fundamental analysis digs deeper into the reasons behind those price changes.
It assesses the financial health of companies, market conditions, and broader economic indicators to predict future price movements.
The Core Components of Fundamental Analysis
Company Financials
- Income Statement: This reflects a company’s profitability over a specific period. It includes revenue, expenses, and net income, giving you insights into how well a company is managing its operations.
- Balance Sheet: This provides a snapshot of a company’s financial condition at a specific point in time, detailing assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity.
- Cash Flow Statement: This shows how well a company generates cash to fund its operating expenses, investments, and financing activities.
Economic Indicators
- GDP (Gross Domestic Product): A measure of a country’s economic activity, indicating the health of the economy.
- Interest Rates: Central banks’ interest rates affect borrowing costs, consumer spending, and overall economic activity.
- Inflation: Rising inflation can erode purchasing power and affect consumer spending and investment.
Industry Analysis
- Market Trends: Understanding the broader trends within a specific industry helps in identifying sectors with potential for growth or decline.
- Competitive Positioning: Analyzing a company’s competitive advantages within its industry can highlight its potential for long-term success.
Qualitative Factors
- Management Quality: Strong, visionary leadership can drive a company’s success. Some of the methods to gauge management quality is to listen to Company Investor calls and presentations.Screener.in is good sight to do that.
- Brand Value: A strong brand can provide a competitive edge and customer loyalty. Let me break a myth for you, brand value is not how good and grand the advertisements are but does the customer love the product or not? You can follow the scuttlebutt approach to get an estimation of the brand value
- Regulatory Environment: Changes in laws and regulations can significantly impact a company’s operations and profitability.
How Does Fundamental Analysis Help in Swing Trading?
Fundamental analysis provides a solid foundation for making informed trading decisions, offering several key benefits:
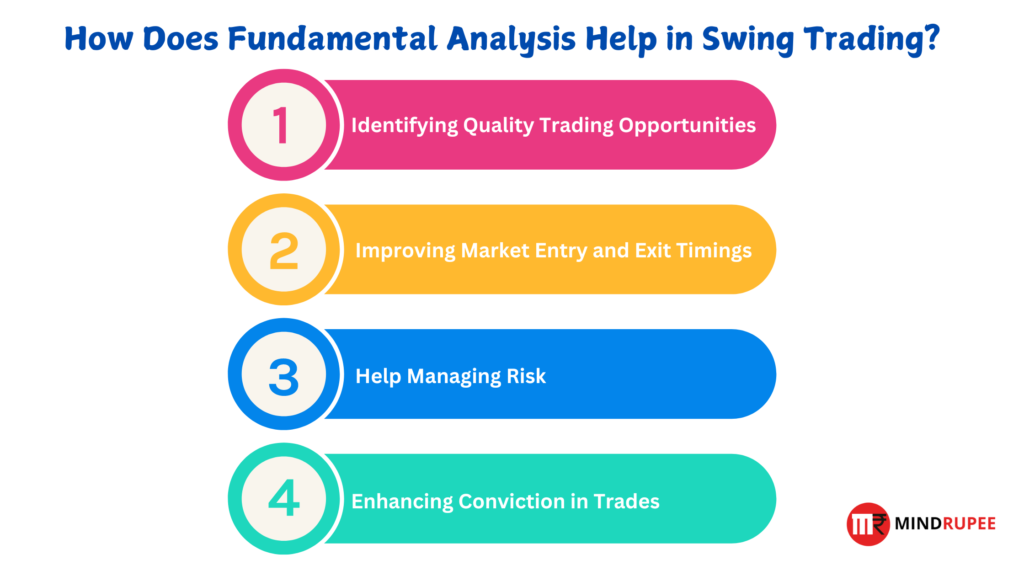
1. Identifying Quality Trading Opportunities
By evaluating a company’s financial health, growth potential, and market position, fundamental analysis helps traders identify stocks with strong underlying value. This ensures that your swing trades are based on solid financials rather than just price movements.
- Example: Consider a company with consistent revenue growth, high profit margins, and low debt. Even if the stock price is currently undervalued due to market sentiment, the strong fundamentals suggest it could rebound, making it a good candidate for a swing trade.
2. Improving Market Entry and Exit Timings
While technical analysis excels in timing trades, fundamental analysis provides the context behind price movements. Understanding why a stock is moving—whether due to earnings reports, economic data, or industry trends—helps you make better decisions about when to enter or exit a trade.
- Example: Suppose a company announces a major new product launch that is expected to significantly boost revenue. A swing trader might enter a position before the product launch, anticipating a price increase.
3. Managing Risk
Fundamental analysis helps you understand the risks associated with a trade by providing insights into a company’s financial stability and the broader economic environment. This allows you to set more informed stop-loss levels and manage your capital effectively.
- Example: If a company is heavily leveraged and operating in a declining industry, fundamental analysis might suggest a higher risk, leading you to either avoid the trade or set a tighter stop-loss.
4. Enhancing Confidence/Conviction in Trades
By understanding the fundamental reasons behind a stock’s price movements, you gain confidence in your trading decisions. This is especially important in swing trading, where holding positions through minor pullbacks can be challenging.
- Example: If a stock with strong fundamentals experiences a temporary dip due to market volatility, your fundamental analysis might give you the confidence to hold the position, knowing the long-term outlook is positive.
When Should You Use Fundamental Analysis in Swing Trading?
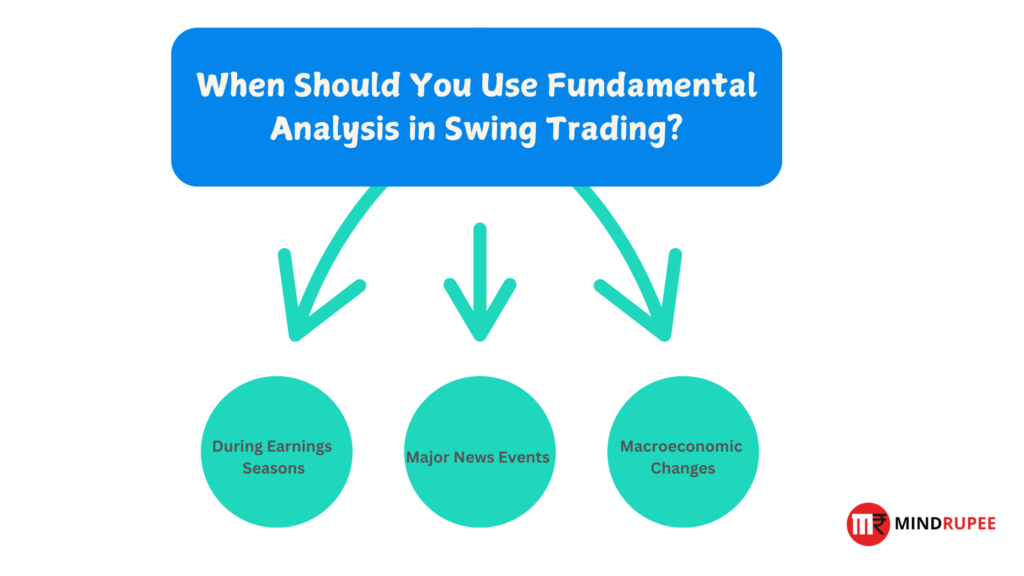
Fundamental analysis can be particularly valuable in specific situations:
1. During Earnings Seasons
Earnings season is when publicly traded companies release their quarterly or annual earnings reports. These reports can cause significant price movements as markets react to whether companies have met, exceeded, or fallen short of expectations.
- Example: A swing trader(A swing trader is someone who buys and sells stocks or other assets in an attempt to profit from short-term price fluctuations in the market. Swing traders try to capture gains from price swings that last at least one day and up to several weeks.) might analyze a company’s historical earnings performance, current industry trends, and recent news to predict whether the upcoming earnings report will likely beat expectations. If the fundamentals are strong, the trader might enter a position before the earnings release, expecting a positive market reaction. Or can build a position post results based on the Results.
2. In Response to Major News Events
News events, such as mergers, acquisitions, product launches, or regulatory changes, can drastically affect a company’s stock price. Fundamental analysis helps you understand the potential impact of these events on the company’s financial health and future prospects.
- Example: If a company announces a merger that is expected to create significant synergies and cost savings, fundamental analysis might suggest that the stock is undervalued, presenting a swing trading opportunity.
3. Amid Macroeconomic Changes
Changes in macroeconomic conditions, such as interest rate hikes, inflation, or changes in government policy, can affect entire sectors or markets. Fundamental analysis allows you to assess how these changes will impact the companies you’re considering for swing trades.
- Example: If the central bank raises interest rates, companies with high debt levels might struggle with higher borrowing costs. A swing trader could use fundamental analysis to avoid or short these companies.
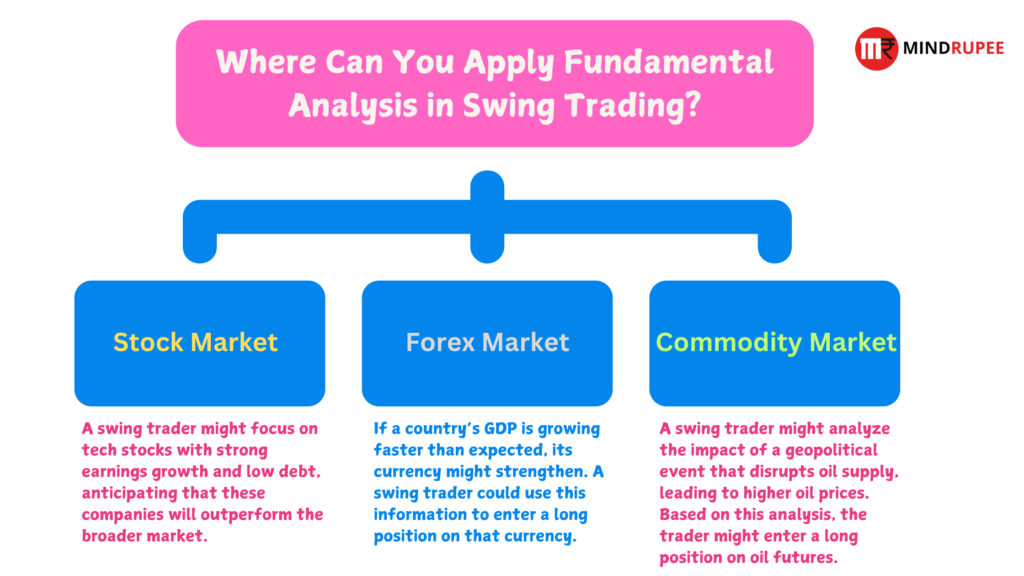
Where Can You Apply Fundamental Analysis in Swing Trading?
Fundamental analysis is versatile and can be applied across various markets and asset classes:
1. Stock Market
In the stock market, fundamental analysis is crucial for evaluating the financial health and growth potential of companies. This involves analyzing financial statements, industry trends, and broader market conditions.
- Example: A swing trader might focus on tech stocks with strong earnings growth and low debt, anticipating that these companies will outperform the broader market.
2. Forex Market
In forex trading, fundamental analysis involves assessing economic indicators, such as GDP, inflation, and interest rates, to predict currency movements. Understanding a country’s economic health can provide insights into the likely direction of its currency.
- Example: If a country’s GDP is growing faster than expected, its currency might strengthen. A swing trader could use this information to enter a long position on that currency.
3. Commodity Market
For commodities, fundamental analysis might focus on supply and demand factors, geopolitical events, and economic indicators that influence commodity prices. Understanding these factors can help you predict price movements in commodities like oil, gold, or agricultural products.
- Example: A swing trader might analyze the impact of a geopolitical event that disrupts oil supply, leading to higher oil prices. Based on this analysis, the trader might enter a long position on oil futures.
Who Should Use Fundamental Analysis in Swing Trading?
Fundamental analysis can be beneficial for various types of traders:
1. Traders Seeking Informed Decisions
Swing traders who want to base their trades on more than just chart patterns can benefit from fundamental analysis. It provides a deeper understanding of the factors driving price movements, allowing for more informed trading decisions. Most importantly helps build conviction.
- Example: A swing trader might use fundamental analysis to select stocks with strong earnings growth and positive cash flow, increasing the likelihood of a successful trade.
2. Risk-Averse Investors
Investors who prefer to minimize risk can use fundamental analysis to ensure they are trading fundamentally sound securities. This approach helps avoid stocks that might be technically attractive but fundamentally weak.
- Example: A risk-averse swing trader might focus on blue-chip stocks with strong balance sheets and consistent dividend payouts, reducing the risk of significant losses.
3. Experienced Traders
Traders with a solid understanding of both technical and fundamental analysis can use the latter to refine their trading strategies. By combining both approaches, they can increase the probability of successful trades.
- Example: An experienced swing trader might use technical analysis to identify potential entry points and then use fundamental analysis to confirm the trade by ensuring the company has strong financials.
So in crux all types of traders can use it for varied purpose.
How to Incorporate Fundamental Analysis into Swing Trading
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s dive into the practical steps of incorporating fundamental analysis into your swing trading strategy.
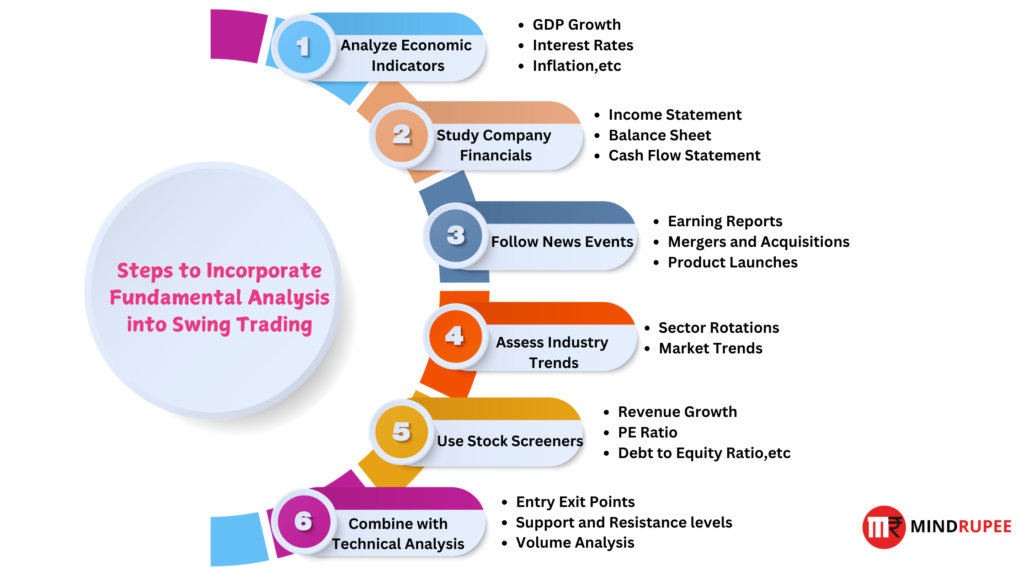
1. Analyze Economic Indicators
Economic indicators provide valuable insights into the broader market environment, helping traders predict potential price movements in various asset classes.
- GDP Growth: A strong GDP growth rate indicates a robust economy, which can lead to higher stock prices and a stronger currency. Conversely, a declining GDP may signal economic troubles ahead.
- Interest Rates: Central banks use interest rates to control inflation and economic growth. Lower interest rates generally stimulate spending and investment, boosting stock prices, while higher rates can have the opposite effect.
- Inflation: Rising inflation can erode purchasing power and reduce consumer spending, negatively impacting company profits. Understanding inflation trends can help swing traders anticipate market movements.
Example: If GDP growth is accelerating and inflation is stable, a swing trader might look for buying opportunities in consumer discretionary stocks, expecting increased consumer spending.
2. Study Company Financials
Company financials are the cornerstone of fundamental analysis. By analyzing financial statements, traders can assess a company’s profitability, financial health, and growth prospects.
- Income Statement: Focus on revenue, operating income, and net income to evaluate a company’s profitability. Consistent revenue and profit growth are positive indicators for swing traders.
- Balance Sheet: Analyze assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity to understand a company’s financial condition. A strong balance sheet with low debt and high equity suggests financial stability.
- Cash Flow Statement: Evaluate the cash flow from operations, investing, and financing activities. Positive cash flow indicates a company’s ability to sustain its operations and invest in growth.
Example: A swing trader might focus on a company with increasing revenues and strong free cash flow, expecting that these fundamentals will support a rising stock price.
3. Follow News Events
News events can act as catalysts for short-term price movements. By staying updated on news related to the stocks you’re trading, you can capitalize on market reactions.
- Earnings Reports: Analyze earnings reports to assess whether a company is likely to beat, meet, or miss market expectations. Positive earnings surprises can lead to price spikes, while negative surprises can result in declines.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: M&A activity can significantly impact stock prices. A well-executed merger can create synergies and cost savings, boosting the combined company’s stock price.
- Product Launches: New product launches, especially in tech or pharmaceutical sectors, can drive significant price movements. Analyze the potential market impact of the product to assess the stock’s future direction.
Example: If a company announces a major acquisition that is expected to enhance its market position, a swing trader might enter a long position, anticipating a positive market reaction.
4. Assess Industry Trends
Industry trends can provide valuable insights into the future performance of individual companies. By understanding the broader market environment, traders can identify sectors with growth potential or those facing challenges.
- Sector Rotation: In certain economic conditions, investors might rotate their investments from one sector to another. For example, during an economic expansion, cyclical sectors like technology and consumer discretionary often outperform, while defensive sectors like utilities and healthcare might lag.
- Market Trends: Identify emerging trends within an industry, such as the shift towards renewable energy or the increasing adoption of e-commerce. Companies positioned to benefit from these trends may present attractive swing trading opportunities.
Example: A swing trader might focus on renewable energy stocks as governments and businesses shift towards cleaner energy sources. By identifying companies with strong financials and technological advantages in this sector, the trader can capitalize on this long-term trend.
5. Use Stock Screeners
Stock screeners allow traders to filter stocks based on specific fundamental criteria, making it easier to identify potential trading opportunities.
- Revenue Growth: Screen for stocks with strong revenue growth, indicating that the company is expanding its market share and generating higher sales.
- P/E Ratio: A low P/E ratio compared to industry peers might indicate an undervalued stock, while a high P/E ratio could suggest overvaluation.
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: A low debt-to-equity ratio suggests that a company is not overly reliant on debt to finance its operations, reducing financial risk.
- Note : These ratios shall not be used in isolation rather shall be used in conjunction.
Example: A swing trader might use a stock screener to identify companies with a minimum annual revenue growth rate of 15%, focusing on those that also have a low debt-to-equity ratio and a reasonable P/E ratio.
6. Combine with Technical Analysis
While fundamental analysis helps identify which stocks to trade, technical analysis helps determine when to trade. Combining these two approaches can improve your trading success.
- Entry and Exit Points: Use technical indicators like moving averages, RSI, and MACD to time your trades. For example, if fundamental analysis suggests a stock is undervalued, wait for a technical signal (e.g., a bullish crossover) before entering the trade.
- Support and Resistance Levels: Identify key support and resistance levels on the chart to set stop-loss and take-profit levels. This helps protect your capital and lock in profits.
- Volume Analysis: Use volume indicators to confirm the strength of a price movement. A price increase with high volume is more likely to be sustained than one with low volume.
Example: After conducting fundamental analysis, a swing trader might identify a stock with strong earnings growth. They could then wait for the stock to break through a key resistance level with high volume before entering the trade.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
To further illustrate how fundamental analysis can be applied in swing trading, let’s explore a few real-world examples:
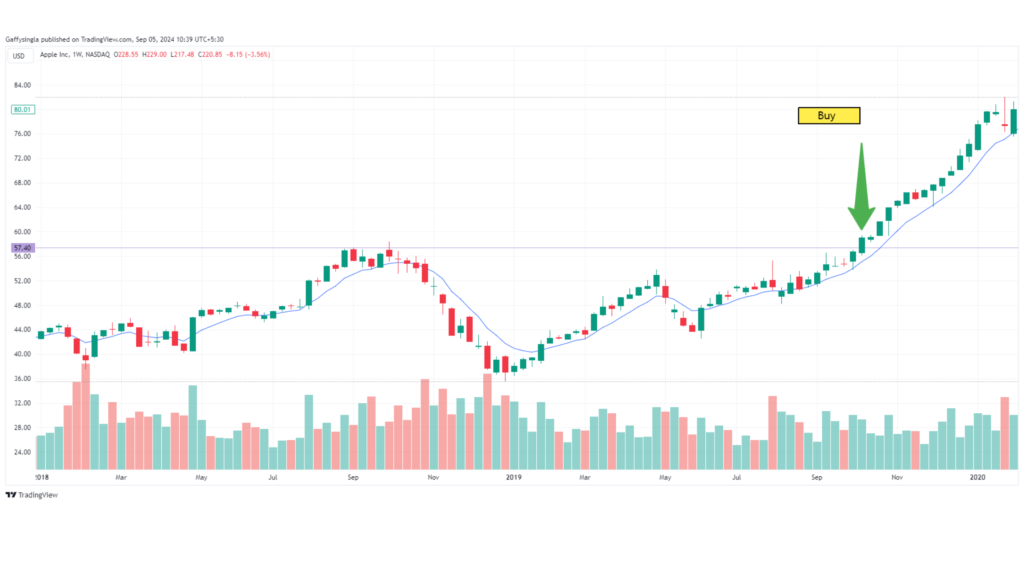
1. Case Study: Apple Inc. (AAPL)
In late 2019, Apple announced strong earnings and record revenue from its iPhone sales, particularly in the Chinese market. The company’s fundamentals were strong, with increasing revenue, profit margins, and cash flow. At the same time, technical analysis showed a bullish trend with the stock breaking out of a consolidation pattern.
- Action: A swing trader might have used this combination of strong fundamentals and bullish technical indicators to enter a long position on Apple, riding the stock’s upward momentum over the next few weeks.
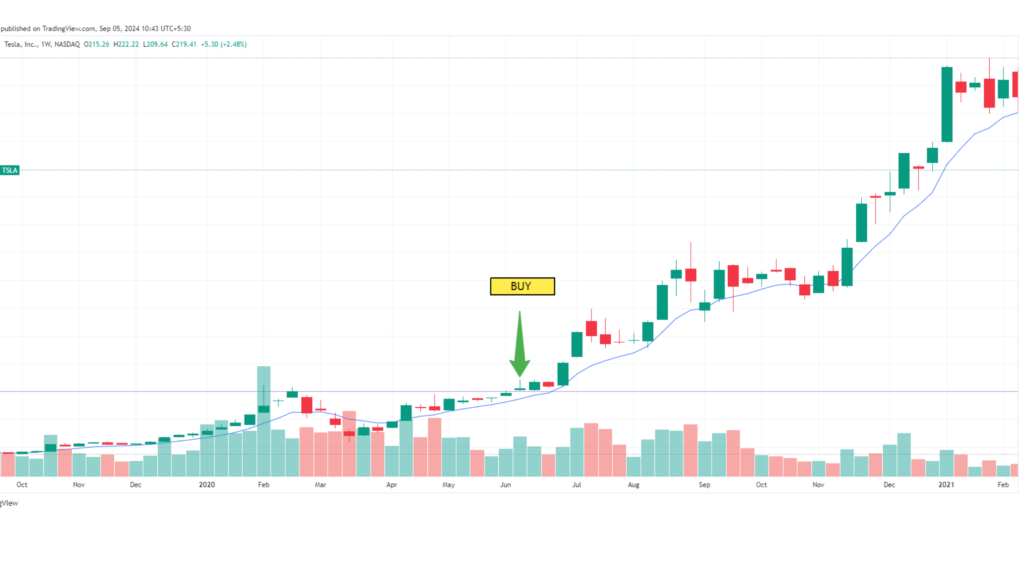
2. Case Study: Tesla Inc. (TSLA)
Tesla’s stock has been highly volatile, driven by a mix of strong fundamentals (e.g., increasing sales and expansion into new markets) and speculative market behavior. In early 2020, Tesla announced better-than-expected quarterly earnings and significant progress in its production and delivery targets.
- Action: A swing trader analyzing Tesla’s fundamentals might have noticed the company’s strong revenue growth and future potential in the electric vehicle market. Combining this with technical analysis showing a breakout above a key resistance level, the trader could have entered a position, benefiting from the subsequent price surge.
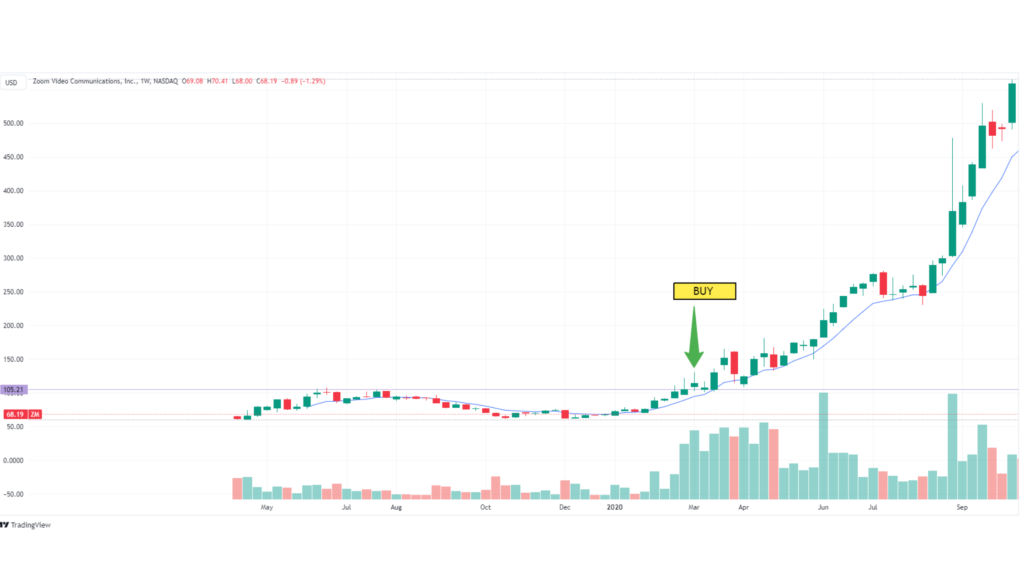
3. Case Study: Zoom Video Communications (ZM)
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Zoom’s user base and revenue grew exponentially as remote work and online communication became the norm. The company’s fundamentals showed significant revenue growth and profitability, while technical analysis revealed a strong uptrend.
- Action: A swing trader could have identified Zoom as a strong candidate for a swing trade, entering a position during a pullback and riding the stock’s momentum as it continued to rise.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Fundamental Analysis
While fundamental analysis can significantly enhance your swing trading strategy, it’s essential to avoid common pitfalls:
1. Overemphasizing Short-Term Data
Swing traders often hold positions for several days to weeks, making it important not to overemphasize short-term data or news that might not have a lasting impact on a stock’s price.
- Example: Avoid making trading decisions based solely on a single news event without considering the company’s overall fundamentals.
2. Ignoring Market Sentiment
Even if a stock has strong fundamentals, market sentiment can drive prices in the short term. Ignoring market sentiment can lead to mistimed trades.
- Example: A fundamentally strong stock might still decline if market sentiment is negative due to broader economic concerns.
3. Failing to Combine with Technical Analysis
Relying solely on Fundamental Analysis without considering technical indicators can result in poorly timed trades.
- Example: Even if a stock is fundamentally sound, entering a trade without considering technical signals like support and resistance levels can lead to suboptimal entry points.
Conclusion
Incorporating fundamental analysis into your swing trading strategy provides a comprehensive approach to trading, combining the power of financial insights with the precision of technical analysis.
By understanding the underlying factors that drive price movements, you can make more informed trading decisions, manage risks effectively, and ultimately enhance your profitability.
Whether you’re a novice trader looking to refine your strategy or an experienced trader seeking to add another layer of analysis to your trades, fundamental analysis is a powerful tool that can give you a competitive edge in the markets.
By staying informed, conducting thorough research, and combining both fundamental and technical analysis, you can navigate the complexities of swing trading with greater confidence and success.
Final Thoughts
Mastering swing trading requires a balanced approach that leverages both technical and fundamental insights. While technical analysis helps you time the market, fundamental analysis gives you the conviction to hold onto your trades and avoid common pitfalls.
By integrating these two approaches, you can build a robust trading strategy that adapts to market conditions and enhances your trading outcomes.
Remember, successful trading is not just about predicting price movements but understanding the reasons behind them.
By focusing on the fundamentals, you can ensure that your trades are based on solid financial principles, increasing your chances of success in the ever-changing world of swing trading.
Happy Trading!!